DAT380 Advanced Database Architecture
DAT380 Advanced Database Architecture
DAT380 covers database concepts. Topics include data structures, schemas and standards in addition to centralized and client server systems, server system architectures, parallel systems, distributed systems.
-
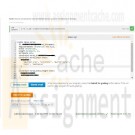
DAT/380 Week 3 LAB 3.10 - Create Horse table with constraints
Regular Price: $5.00
Special Price $3.00
DAT/380 Week 3 LAB 3.10 - Create Horse table with constraints
Create a Horse table with the following columns, data types, and constraints. NULL is allowed unless 'not NULL' is explicitly stated.
ID - integer with range 0 to 65 thousand, auto increment, primary key
RegisteredName - variable-length string with max 15 chars, not NULL
Breed - variable-length string with max 20 chars, must be one of the following: Egyptian Arab, Holsteiner, Quarter Horse, Paint, Saddlebred
Height - number with 3 significant digits and 1 decimal place, must be ≥ 10.0 and ≤ 20.0
BirthDate - date, must be ≥ Jan 1, 2015Note: Not all constraints can be tested due to current limitations of MySQL.
Learn More -
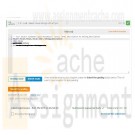
DAT/380 Week 2 LAB 2.10 - Select employees and managers with inner join
Regular Price: $5.00
Special Price $3.00
DAT/380 Week 2 LAB 2.10 - Select employees and managers with inner join
The Employee table has the following columns:
ID - integer, primary key
FirstName - variable-length string
LastName - variable-length string
ManagerID - integer
Write a SELECT statement to show a list of all employees' first names and their managers' first names. List only employees that have a manager. Order the results by Employee first name. Use aliases to give the result columns distinctly different names, like "Employee" and "Manager".Hint: Join the Employee table to itself using INNER JOIN.
Learn More -
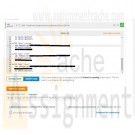
DAT/380 Week 5 LAB 5.7 - Implement supertype and subtype entities (Sakila)
Regular Price: $5.00
Special Price $3.00
DAT/380 Week 5 LAB 5.7 - Implement supertype and subtype entities (Sakila)
Refer to the customer and staff tables of the Sakila database. These tables have many columns in common and represent similar entities. Convert the customer and staff entities into subtypes of a new supertype person:
In the center is the person entity, with primary key person_id and additional attributes first_name, last_name, email, active, and last_update. The person entity contains subtype entities staff and customer. The staff entity has primary key person_id and additional attributes picture, username, and password. The customer entity has primary key person_id and additional attribute create_date. Cardinality does not appear after the primary keys and attributes. On the left is the address entity, connected to the person entity by the belongs_to relationship. Belongs_to has cardinality 1(1) on the address side and M(0) on the person side. On the right is the store entity, connected to the person entity by the works_at relationship. Works_at has cardinality 1(1) on the store side and M(0) on the person side.
The diagram uses Sakila naming conventions. Follow the Sakila conventions for your table and column names:
All lower case
Underscore separator between root and suffix
Foreign keys have the same name as referenced primary keyImplement supertype and subtype entities as person, customer, and staff tables with primary key person_id.
Implement attributes as columns:
All columns are NOT NULL.
The person_id columns have data type SMALLINT UNSIGNED.
The last_update and create_date columns have data type TIMESTAMP.
The picture column has data type BLOB.
All other columns have data type VARCHAR(20).Implement the dependency relationships between subtype and supertype entities as foreign keys:
The person_id columns of customer and staff become foreign keys referring to person.
Specify CASCADE actions for both relationships.Implement the belongs_to and works_at relationships as foreign keys:
belongs_to becomes an address_id foreign key in person referring to address.
works_at becomes a store_id foreign key in staff referring to store.
Specify RESTRICT actions for both relationships.The address and store tables, with primary keys address_id and store_id, are pre-defined in the zyLab environment. Foreign keys must have the same data types as the referenced primary keys:
address_id has data type SMALLINT UNSIGNED.
store_id has data type TINYINT UNSIGNED.If you execute your solution with the Sakila database, you must first drop customer, staff, and all constraints that refer to these tables. Use the following statements with Sakila only, not in the zyLab environment:
Learn More
DROP TABLE customer, staff;
ALTER TABLE payment
DROP CONSTRAINT fk_payment_customer,
DROP CONSTRAINT fk_payment_staff;
ALTER TABLE rental
DROP CONSTRAINT fk_rental_customer,
DROP CONSTRAINT fk_rental_staff;
ALTER TABLE store
DROP CONSTRAINT fk_store_staff;





