Search results for 'using'
-

DAT 210 Week 1 Create an algorithm using pseudocode
Regular Price: $10.00
Special Price $8.00
DAT 210 Week 1 Create an algorithm using pseudocode
You work in the IT group of a department store and the latest analytics shows there is a bug that allows customers to go over their credit limit. The company's president has asked you to develop a new algorithm to solve this problem.
Create your algorithm using pseudocode that determines if a department store customer has exceeded their credit limit. Be sure you gather the following inputs from the user:
Account number
Balance of the account
Total cost of all the products the customer is looking to purchase
Allowed credit limitAfter you gather the inputs, make sure your algorithm calculates if the user can purchase the products and provides a message to the user indicating if the purchase is approved or declined.
Document your answers in a Microsoft® Word document.
Review "Understanding Object-Oriented Programming" with Jungwoo Ryoo from Lynda.com® for additional guidance.
Submit your document.
Learn More -
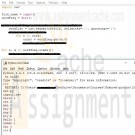
Python 10.9 LAB: Word frequencies (lists)
Regular Price: $10.00
Special Price $8.00
Python 10.9 LAB: Word frequencies (lists)
Write a program that first reads in the name of an input file and then reads the file using the csv.reader() method. The file contains a list of words separated by commas. Your program should output the words and their frequencies (the number of times each word appears in the file) without any duplicates.
Ex: If the input is:
input1.csvand the contents of input1.csv are:
hello,cat,man,hey,dog,boy,Hello,man,cat,woman,dog,Cat,hey,boythe output is:
hello 1
cat 2
man 2
hey 2
dog 2
boy 2
Hello 1
woman 1
Cat 1Note: There is a newline at the end of the output, and input1.csv is available to download.
Learn More -

PRG/211 Week 1 Lab 3.8: Using math functions
Regular Price: $8.00
Special Price $3.00
PRG/211 Week 1 Lab 3.8.1: Using math functions
Given three floating-point numbers x, y, and z, output x to the power of y, x to the power of (y to the power of z), the absolute value of x, and the square root of (xy to the power of z).
Ex: If the input is 5.0 6.5 3.2, the output is:
34938.56214843421 1.2995143401732918e+279 5.0 262.42993783925596
Learn More
Hint: Coral has built-in math functions (discussed elsewhere) that may be used. -

PRG/211 Week 1 Lab 3.5: Divide by x
Regular Price: $8.00
Special Price $3.00
PRG/211 Week 1 Lab 3.5.1: Divide by x.
Write a program using integers userNum and x as input, and output userNum divided by x four times.
Ex: If the input is 2000 2, the output is:
1000 500 250 125
Learn More
Note: In Coral, integer division discards fractions. Ex: 6 / 4 is 1 (the 0.5 is discarded). -
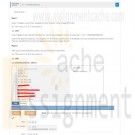
PRG/211 Week 1 Lab 3.7: Simple statistics
Regular Price: $8.00
Special Price $3.00
PRG/211 Week 1 Lab 3.7.1: Simple statistics
Part 1
Given 3 integers, output their average and their product, using integer arithmetic.Ex: If the input is 10 20 5, the output is:
11 1000
Note: Integer division discards the fraction. Hence the average of 10 20 5 is output as 11, not 11.666666666666666.Submit the above for grading. Your program will fail the test cases (which is expected), until you complete part 2 below but check that you are getting the correct average and product using integer division.
Part 2
Also output the average and product, using floating-point arithmetic.Ex: If the input is 10 20 5, the output is:
11 1000
Learn More
11.666666666666666 1000.0 -
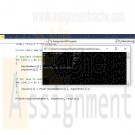
CSIS 209 Programming Assignment 4
Regular Price: $10.00
Special Price $8.00
CSIS 209 Programming Assignment 4
Adapted from: Deitel & Deitel (2017). Visual C# 2015 How to Program (6th ed.). Pearson Education, Inc.
Write a recursive method called Power(base, exponent) that, when called, returns base exponent.
For example, Power ( 3, 4 ) = 3 * 3 * 3 * 3.
Assume that exponent is an integer greater than or equal to 1. The recursion step should use the relationship:
base exponent = base * base exponent - 1
The terminating condition occurs when exponent is equal to 1 because
base1 = base
Incorporate this method into an application that enables the user to enter the base and exponent.Requirements:
In the Main() method, declare three arrays of long data types: baseNumbers, exponents, and results. Each array should be created to hold exactly 5 members.Using a FOR loop, populate the baseNumbers array with random integers between 1 and 50 and populate the exponents array with random integers between 1 and 10. Use a random number generator to create these random numbers.
Using another FOR loop, call the Power method, passing it a member of the baseNumbers array and a member of the exponents array for each iteration of the loop. Store the returned values in the results array.
The Power method should use the algorithm described above and MUST be recursive, taking two longs as arguments and returning a long data type.
Create another method called PrintArrays that takes as arguments the three arrays you created above and returns void. The method should print a header as "Base", "Exponent", and "Result" with each word separated with a single tab character. Using a FOR loop, iterate over each array using the GetUpperBound method to determine the condition for which the loop terminates. For each iteration of the loop, print out the base, exponent, and result from each array under the appropriate column headings. (Hint: You may need to use one or more tabs to separate the data values to make them line up with the headers above.)
The Main() method should call the PrintArrays method, passing in the three arrays as arguments.
Learn More -

CSIS 209 Programming Assignment 3
Regular Price: $10.00
Special Price $8.00
CSIS 209 Programming Assignment 3
Adapted from: Deitel & Deitel (2017). Visual C# 2015 How to Program (6th ed.).Pearson Education, Inc.
Write an application to simulate the rolling of two dice. The app should use an object of class Random one to the first die and again to roll the second die. The sum of the two values should then be calculated. Each die can show an integer from 1 to 6, so the sum of the values will vary from 2 to 12, with 7 being the most frequest sum and 2 and 12 the least frequest sums.
Your application should roll the dice 36,000 times. Use a one-dimensional array to tally the number of times each possible sum appears. Display the results in tabular format. Determine whether or the totals are reasonable (e.g. there are six ways to roll a 7, so approximately one-sixth of the rolls should be 7).
Requirements:
In the Main() method, you will declare an integer array to hold the tally of the rolls. Use the Random class to generate a random number between 1 and 6 for each of the die rolls.Using a FOR loop, iterate 36,000 times to make the two die rolls, sum the results, then increase the count of the correct element in the array to record the result. (HINT: The array being used here WILL NOT be 36,000 elements long. It will only have a length of 10)
Using another FOR loop, print the results of roll counts contained in the array to the screen in two columns with headers. The first column will hold all the possible rolls of the two dice, with the count of how many times that roll combination was achieved in the second column.
When using the loop to print the results array, use the GetUpperBounds() method to determine how many times to loop. DO NOT assume that you will always get an array of length 10. Make the code smart enough to figure out how many times to loop no matter what the length of the array.
Learn More -

CSIS 209 Programming Assignment 2 Salesperson Total Sales Application
Regular Price: $15.00
Special Price $12.00
CSIS 209 Programming Assignment 2 Salesperson Total Sales Application
Adapted from: Deitel & Deitel (2017). Visual C# 2015 How to Program (6th ed.). Pearson Education, Inc.
A large company pays its salespeople on a commission basis. The salespeople receive $200 per week plus 9% of their gross sales for that week. For example, a salesperson who sells $5,000 worth of merchandise in a week receives $200 plus 9% of $5,000, or a total of $650. You’ve been supplied with a list of the items sold by each salesperson. The values of these items are as follows:
Item Value
1 239.99
2 129.75
3 99.95
4 350.89Develop a C# application that inputs one salesperson's items sold for the last week, then calculates and displays that salesperson's total sales. There's no limit to the number of items that can be sold by a salesperson. You do not have to implement this with classes and objects.
Technical Requirements:
Prompt the user to enter the salesperson's name, and store this name in a variable.
Prompt the user to enter an item number and a quantity sold of that item. Store these two entries in two separate variables called "intItem" and "intQuantity".
Using a DO-WHILE control structure, loop until the user enters -1 for the item number.
Calculate the amount of sales for an item and store the result in a variable called dblItemSales.
After the user enters an item number and a quantity, print to the screen: the salesperson's name "has sold " [intQuantity] "of item # [intItem].
Accumulate the total sales in a variable called dblTotalSales by using a SWITCH statement to select the correct value to be multiplied by the quantity sold and adding this result to a running total, which is stored in the variable dblTotalSales.
If the user enters a number other than 1, 2, 3, or 4, display the message "Invalid Entry" and re-prompt the user to enter an Item Number. Make sure you do not perform any calculations or prompt the user to enter a quantity if the item number is incorrect.
After accumulating the total sales for an employee (that is, after the user has entered a -1 to quit), print to the screen Salesperson [Salesperson’s name] sold a total of [total sales].See below for examples of the required output.
Learn More -

CYB/130 Week 1 Python LAB 2.32: Using math functions
Regular Price: $8.00
Special Price $3.00
CYB/130 Week 1 Python LAB 2.32: Using math functions
Given three floating-point numbers x, y, and z, output x to the power of z, x to the power of (y to the power of z), the absolute value of (x minus y), and the square root of (x to the power of z).Output each floating-point value with two digits after the decimal point, which can be achieved as follows:
print('{:.2f} {:.2f} {:.2f} {:.2f}'.format(your_value1, your_value2, your_value3, your_value4))Ex: If the input is:
Learn More
5.0
1.5
3.2
Then the output is:
172.47 361.66 3.50 13.13 -

CYB/130 Week 1 Python LAB 2.31: Expression for calories burned during workout
Regular Price: $8.00
Special Price $3.00
CYB/130 Week 1 Python LAB 2.31: Expression for calories burned during workout
The following equations estimate the calories burned when exercising (source):Women: Calories = ( (Age x 0.074) — (Weight x 0.05741) + (Heart Rate x 0.4472) — 20.4022 ) x Time / 4.184
Men: Calories = ( (Age x 0.2017) + (Weight x 0.09036) + (Heart Rate x 0.6309) — 55.0969 ) x Time / 4.184
Write a program using inputs age (years), weight (pounds), heart rate (beats per minute), and time (minutes), respectively. Output calories burned for women and men.
Output each floating-point value with two digits after the decimal point, which can be achieved as follows:
print('Men: {:.2f} calories'.format(calories_man))Ex: If the input is:
Learn More
49
155
148
60
Then the output is:
Women: 580.94 calories
Men: 891.47 calories





