Search results for 'WK9D1 apply your knowledge Chapter 5: Apply Your Knowledge – Adding Fields Babbage CPA Firm database'
Maximum words count is 10. In your search query was cut next part: Adding Fields Babbage CPA Firm database.
-
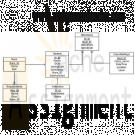
COM 330 Martial Arts R Us (MARU) ERD and Access Database
$20.00“Martial Arts R Us” (MARU) needs a database. MARU is a martial arts school with hundreds of students. It is necessary to keep track of all the different classes that are being offered, who is assigned to teach each class, and which students attend each class. Also, it is important to track the progress of each student as they advance.
Learn More
Create a complete Crow’s Foot ERD for these requirements:
• Students are given a student number when they join the school. This is stored along with their name, date of birth, and the date they joined the school.
• All instructors are also students, but clearly, not all students are instructors. In addition to the normal student information, for each instructor, the date that they start working as an instructor must be recorded, along with their instructor status (compensated or volunteer).
• An instructor may be assigned to teach any number of classes, but each class has one and only one assigned instructor. Some instructors, especially volunteer instructors, may not be assigned to any class.
• A class is offered for a specific level at a specific time, day of the week, and location. For example, one class taught on Mondays at 5:00 pm in Room #1 is an intermediate-level class. Another class taught on Mondays at 6:00 pm in Room #1 is a beginner-level class. A third class taught on Tuesdays at 5:00 pm in Room #2 is an advanced-level class.
• Students may attend any class of the appropriate level during each week so there is no expectation that any particular student will attend any particular class session. Therefore, the actual attendance of students at each individual class meeting must be tracked.
• A student will attend many different class meetings; and each class meeting is normally attended by many students. Some class meetings may have no students show up for that meeting. New students may not have attended any class meetings yet.
• At any given meeting of a class, instructors other than the assigned instructor may show up to help. Therefore, a given class meeting may have several instructors (a head instructor and many assistant instructors), but it will always have at least the one instructor that is assigned to that class. For each class meeting, the date that the class was taught and the instructors’ roles (head instructor or assistant instructor) need to be recorded. For example, Mr. Jones is assigned to teach the Monday, 5:00 pm, intermediate class in Room #1. During one particular meeting of that class, Mr. Jones was present as the head instructor and Ms. Chen came to help as an assistant instructor.
• Each student holds a rank in the martial arts. The rank name, belt color, and rank requirements are stored. Each rank will have numerous rank requirements. Each requirement is considered a requirement just for the rank at which the requirement is introduced. Every requirement is associated with a particular rank. All ranks except white belt have at least one requirement.
• A given rank may be held by many students. While it is customary to think of a student as having a single rank, it is necessary to track each student’s progress through the ranks. Therefore, every rank that a student attains is kept in the system. New students joining the school are automatically given a white belt rank. The date that a student is awarded each rank should be kept in the system. All ranks have at least one student that has achieved that rank at some time. -

Murachs SQL for SQL Server Chapter 10 How to create and maintain databases and tables with SQL statements
$12.00Murach’s SQL for SQL Server Chapter 10 How to create and maintain databases and tables with SQL statements
Learn More
Exercises
1. Create a new database named Membership.
2. Write the CREATE TABLE statements needed to implement the following design in the Membership database. Include reference constraints. Define IndividualID and GroupID with the IDENTITY keyword. Decide which columns should allow null values, if any, and explain your decisions. Define the Dues column with a default of zero and a check constraint to allow only positive values.
3. Write the CREATE INDEX statements to create a clustered index on the GroupID column and a nonclustered index on the IndividualID column of the GroupMembership table.
4. Write an ALTER TABLE statement that adds a new column, DuesPaid, to the Individuals table. Use the bit data type, disallow null values, and assign a default Boolean value of False.
5. Write an ALTER TABLE statement that adds two new check constraints to the Invoices table of the AP database. The first should allow (1) PaymentDate to be null only if PaymentTotal is zero and (2) PaymentDate to be not null only if PaymentTotal is greater than zero. The second constraint should prevent the sum of PaymentTotal and CreditTotal from being greater than InvoiceTotal.
6. Delete the GroupMembership table from the Membership database. Then write a CREATE TABLE statement that recreates the table, this time with a unique constraint that prevents an individual from being a member in the same group twice. -

CS362 Structured Query Language for Data Management Week 2 IP
$20.00CS362 Structured Query Language for Data Management Week 2 IP
Learn More
After creating the database schema, use Insert, Update, and Delete commands to populate the tables with the following information.
1. Insert the following classes' records:
Code Name Description
ACCT306 Accounting 1 This course introduces accounting concepts and explores the accounting environment. It covers the basic structure of accounting, how to maintain accounts, use account balances to prepare financial statements, and complete the accounting cycle. It also introduces the concept of internal control and how to account for assets.
CS362 Structured Query Language for Data Management This course gives complete coverage of SQL, with an emphasis on storage, retrieval, and manipulation of data.
ENG115 English Composition In this course, students focus on developing writing skills through practice and revision. Students will examine expository, critical, and persuasive essay techniques.
FIN322 Investments This course focuses on investments and investment strategies. Various investment vehicles such as stocks, bonds, and commodities are examined. Students will explore the principles of security analysis and valuation.
2. Insert the following advisors' records:
Name Email
Fred Stone fred@college.edu
Bob Gordon bob@college.edu
Jack Simpson jack@college.edu
3. Insert the following students' records:
Name Birthdate Gender StartDate GPA IsActive AdvisorID
Craig Franklin 1970-03-15 Male 2010-05-30 3.10 Yes 3
Harriet Smith 1982-04-15 Female 2010-05-30 3.22 Yes 1
George David 1984-11-05 Male 2010-10-01 0.00 Yes 3
Ben Jefferson 1976-09-25 Male 2009-02-21 1.80 No, the student has gone on temporary leave to pursue other opportunities but plans on returning in 1 year. 3
4. Delete the course named Investments from the system.
5. Change Harriet Smith’s birthdate to April 25, 1982 and her GPA to 3.25.
Copy and paste the work into your Key Assignment document and include screen shots of each step, describe what you did for each step and paste in the actual SQL text used to perform each step. Provide an introduction explaining the important of these commands in relation to your overall Key Assignment. -
CS362 Structured Query Language for Data Management Week 3 IP Select Statements
$20.00CS362 Structured Query Language for Data Management Week 3 IP Select Statements:
Learn More
Provide select statements to satisfy the following data requests:
1. List all active male students assigned to Advisors 1 or 3 (Fred Stone or Jack Simpson). (Where Clause - Filtering 3 different things: Active, Male Students, Adivsors)
2. Provide a list of all students without a biography. (focusing Null Biography)
3. What classes are in the English department? (Where Clause)
4. Create a list of all students and their advisors. Sort by the advisor’s name and then the student’s name. Include the student’s birth date, gender, and GPA. (join's statement combine the two tables students and class tables: Order by clause like birthday, gpa,etc)
5. How many students were born in the 1980s? (Aggregate using count expression)
6. Write a query to show the average GPA by gender. (Aggregate using count expression)
7. Provide a list of all advisors and the number of active students assigned to each. Filter out any advisors with more than 1 student. (Combine lines 4-6)
Copy and paste the work into your Key Assignment document and include screen shots of each step, describe what you did for each step and paste in the actual SQL text used to perform each step. Include an explanation as to how and where these queries or others like them can be used in your final system. Upload your document to the Submitted Tasks. -
CS362 Structured Query Language for Data Management Week 4 IP Extend the Design
$20.00CS362 Structured Query Language for Data Management Week 4 IP Extend the Design
Learn More
Using your Week 1 IP as a starting point, extend the design to accommodate degree programs. The new design should incorporate the following functionalities:
1. A degree has a name and description.
2. What degree is the student working towards? A student can only work on one degree at a time.
3. What classes are necessary to obtain a specific degree?
4. Provide the DDL script to add the tables for the new design changes. Include an updated diagram that shows all the tables in the system.
5. Write the DML script to insert 3 test records in each of the tables in the system. This data will be necessary to write the queries in the next assignment.
Copy and paste the work into your Key Assignment document and include screen shots of each step, describe what you did for each step and paste in the actual SQL text used to perform each step. Upload your document to the Submitted Tasks section. -
CS362 Structured Query Language for Data Management Week 5 IP Functions Stored Procedure and Indexes
$20.00CS362 Structured Query Language for Data Management Week 5 IP Functions Stored Procedure and Indexes
This assignment requires you to take your extended design from Week 4 IP and add proper indexes, a function, and a stored procedure. Your changes will provide functionality used by the teachers for screens such as a grade book. Be sure any code is properly formatted and has appropriate comments.
Part 1: Function
Write a user-defined function (UDF) that calculates a student's GPA for a given time frame. Inputs are StudentId int, ClassStartDateStart datetime, and ClassStartDateEnd datetime. The output should be the student's GPA for all classes that were taken between ClassStartDateStart and ClassStartDateEnd. Also, supply the script to call this new function, passing it parameter values of your choice.
Part 2: Stored Procedure
Write the DDL script to make a stored procedure that returns data needed to display a grade book screen for a professor. The only input for the stored procedure is a ClassId. Outputs need to include student names and grades for all assignments as well as a calculated overall grade for the class for each student. Provide an example calling this new stored procedure, passing it parameter values of your choice. Include a screenshot of the output.
Part 3: Indexes
Provide a list of suggested indexes and the DDL script to create them. Include an explanation of the purpose of indexes and how you made your decision for the fields to include in your list of suggested indexes.Copy and paste the work into your Key Assignment document and include screen shots of each step, describe what you did for each step and paste in the actual SQL text used to perform each step. Upload your document to the Submitted Tasks.
Learn More -
CS251 Fundamentals of Database Systems Week 4 IP The Microsoft Access Database
$20.00CS251 Fundamentals of Database Systems Week 4 IP The Microsoft Access Database
Learn More
Using Microsoft Access create the tables and relationships defined in your data model. Your Microsoft Access Database at this point should include the following:
The Tables as defined in your Entity Relationship Diagram.
The Relationships between the tables.
3 Defined Queries. One of the queried needs to be created to show the data from the Many-to-Many relationship (or include three tables) originally identified from the initial requirements.
Take a screenshot of the ERD and the Queries.
Add the Screenshots to the section in your template titled: The Microsoft Access Database. -
ITCO231 Unit 5 Individual Project Database SQL Server
$20.00Unit 5 Individual Project Database SQL Server
Learn More
Deliverable Length: 7 SELECT statements; 3 SQL JOIN statements
At this point, you will add data to your database and validate that they loaded properly. In tabular format, include 3 rows for each table, making sure that the primary-key and foreign-key relationships are properly applied.
Next, you will insert the 30 rows of data that you identified (using the concepts you worked on identifying the primary and foreign keys), then perform queries using JOIN syntax of the database.
Task 1: Create 3 rows of data for each table ensuring that the referential integrity is valid.
Task 2: Add the 30 rows of data to the appropriate table in your database (using any appropriate method available).
Task 3: SELECT all columns and all rows of the 10 tables. Create a screenshot of each query and output data, and submit them.
Task 4: Write SELECT statements for the following (include a screenshot of the SQL and its execution, including the resulting data):
Display the employee id, first_name, last_name, and department_name for all employees.
Rows returned
Display the employee id, first_name, last_name, and job title_name for all employees.
Rows returned
Display the employee id, first_name, last_name, department_name, and job title_name for all employees.
Rows returned
Combine all of the SQL statements (text only) and screenshots into a single Word document, and submit it for grading -
Final Project Part IV Using MS Access Learner Care Database
$20.00Final Project Part IV: Using MS Access
1. Based on the design created in Week 2, create the physical design of the database using MS Access.
Learn More
Create tables that represent the entity that you created in Week 2.
Create the required columns with the appropriate data types.
Specify an appropriate primary key for the table.
Specify constraints for columns wherever applicable
2. Enter at least ten records in the database.
3. Query the database.
Create queries to filter records based on various conditions that you can think of. Some queries you can create include:
If your table has an Age column, then create a query to view the records of students of the same age.
If your table has an Address column, then create a query to view the records of students living in the same area.
4. Check if there is a need to redesign the database.
5.Create entry forms for the database.
Create a form that helps you enter records in the table you created.
Ensure that the constraints you applied in the table are also checked in the form.
Suggest a strategy to ensure that the primary key values are not repeated.
6.Create a report that displays records of all students.
Design the database, enter data, run the queries, create the forms, create the reports and submit your database to the Dropbox. In a Word document, share your experience about this design and implementation process and discuss the need and scope for redesigning the database. -
Database Management Midterm RRGroup database
$20.00Database Management Midterm RRGroup database
1. You are creating a database for donations that are made to different non-for-profit agencies by different individuals. The database is made of three tables: Contributors (the list of donors with information about them), Donations (the list of generous gifts) and Agencies (the list of non-for profit organizations that receive gifts).
Learn More
2. Download all the files from the Midterm folder. Remember: it is best to first save them on your local computer before you open them and start working on them.
3. Open the database named RRGroup. It comes with the Contributors table. This is the one you are going to do all work.
4. Populate the Agency table with data from Agency text file.
5. Examine the Gifts Excel file and based on that file design the third table (headings, primary key, data type). Save it as Donations. Populate it with data from the Gifts file. Remember about the Primary Key.
6. Establish relationships between all three tables. Do all that is necessary to have them established. All of them must be “One-To-Many”.
7. Create a form for the Contributors table. Be sure it displays only one record at a time. Save it.
8. Create a query with the following data:
a. Name of the Agency
b. Number of donors.
c. Average amount of donation.
i. Name this query “Average Gift”
9. Create another query with the following data:
a. Donor’s last name
b. Agency name
c. Agency’s city. Provide ability to enter the city you want to view in the query
d. Amount of donation. You want to see donations over $50.
e. You want to see those donations that need to be picked up.
i. Attention: all the criteria must be “AND” – this query should display only those donors that gave gifts to agencies from an entered city and in the amount over $50 and gave gifts that need to be picked up.
ii. Name this query “Gifts in a City”
10. One more query. This time no criteria, only 3 fields: Donor’s last name, Agency Name and amount of donation. Save it as “Query for report”.
11. Create a report for the “Query for report”. Make sure that records are listed by Contributors. All other settings can be left as the default ones. Name the report: List of Contributions.





