Search results for 'ECO Clothesline database from Chapter 4.'
-

CS371 Database Design Week 5 Assignment Chapter 6 Questions
$20.00CS371 Database Design Week 5 Assignment Chapter 6 Questions
Learn More
Chapter 6 Exercises 1 page 154: Use MySQL Workbench to construct the relational diagram for this database.
Chapter 6 Exercises 2 page 154: Use MySQL Workbench to construct the relational diagram for this database.
Chapter 6 Exercise 5 page 155: Submit responses in Word Doc format.
You may submit a single word doc with SQL queries and your models pasted in – OR – submit separate files including PDFs of your models and a word doc with your queries.
Chapter 6 Exercise 1 page 154: Use MySQL Workbench to construct the relational diagram for this database:
1. Leslie’s Auto Sales has a relational database with which it maintains data on its salespersons, its customers, and the automobiles it sells. Each of these three entity types has a unique attribute identifier.
The attributes that it stores are as follows:
• Salesperson Number (unique), Salesperson Name, Salesperson Telephone, Years with Company
• Customer Number (unique), Customer Name, Customer Address, Value of Last Purchase From Us
• Vehicle Identification Number (unique), Manufacturer, Model, Year, Sticker Price Leslie’s also wants to keep track of which salesperson sold
which car to which customer, including the date of the sale and the negotiated price. Construct a relational database for Leslie’s Auto Sales.
Answer:
Chapter 6 Exercise 2 page 154: Use MySQL Workbench to construct the relational diagram for this database.
2. The State of New York certifies firefighters throughout the state and must keep track of all of them, as well as of the state’s fire departments. Each fire department has a unique department number, a name that also identifies its locale (city, county, etc.), the year it was established, and its main telephone number. Each certified firefighter has a unique firefighter number, a name, year of certification, home
telephone number, and a rank (firefighter, fire lieutenant, fire captain, etc.) The state wants to record the fire department for which each firefighter currently works and each firefighter’s supervisor. Supervisors are always higher-ranking certified firefighters.
Construct a relational database for New York’s fire departments and firefighters.
Answer:
Chapter 6 Exercise 5 page 155: Submit responses in Word Doc format.
5. In the General Hardware Corp. database of Figure 6.1, what would happen if:
a. The delete rule between the CUSTOMER and CUSTOMER EMPLOYEE relations is restrict and an attempt is made to delete the record for customer 2198 in the CUSTOMER relation?
b. The delete rule between the CUSTOMER and CUSTOMER EMPLOYEE relations is cascade and an attempt is made to delete the record for customer 2198 in the CUSTOMER relation?
c. The delete rule between the CUSTOMER and CUSTOMER EMPLOYEE relations is set to null and an attempt is made to delete the record for customer 2198 in the CUSTOMER relation?
d. The delete rule between the CUSTOMER and CUSTOMER EMPLOYEE relations is restrict and an attempt is made to delete the record for employee 33779 of customer 2198 in the CUSTOMER EMPLOYEE relation?
e. The delete rule between the CUSTOMER and CUSTOMER EMPLOYEE relations is cascade and an attempt is made to delete the record for employee 33779 of customer 2198 in the CUSTOMER EMPLOYEE relation?
f. The delete rule between the CUSTOMER and CUSTOMER EMPLOYEE relations is set-to-null and an attempt is made to delete the record for employee 33779 of customer 2198 in the CUSTOMER EMPLOYEE relation?
Answer: -
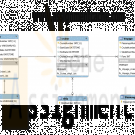
GU CS371 Database Design Week 4 Assignment Chapter 5 Relational Database Model
$20.00GU CS371 Database Design Week 4 Assignment Chapter 5 Relational Database Model
The assignment comes from Chapter 5 Minicase 1 but includes an additional step:
Using MySQL Workbench, create the relational data model for the database for happy cruise lines, which includes 6 tables. (Note: Be sure primary and foreign keys are correct). Export the PDF version of your model for submission.
Then complete steps a – g. Note: On step g, provide correct SQL syntax for finding the result to each item i – viii. i.e. Do not use the informal relational approach – looking for valid, correct SQL as described in Chapter 4.
You may submit a single word doc with SQL queries and your model pasted in – OR – submit 2 separate files including a PDF of your model and a word doc with your queries.Fundamentals of Database Management Systems 2nd Edition Chapter 5 Minicase 1
1. Consider the following relational database for Happy Cruise Lines. It keeps track of ships, cruises, ports, and passengers. A “cruise” is a particular sailing of a ship on a particular date. For example, the seven-day journey of the ship Pride of Tampa that leaves on June 13, 2009, is a cruise. Note the following facts about this environment.
Both ship number and ship name are unique in the SHIP Relation.
A ship goes on many cruises over time. A cruise is associated with a single ship.
A port is identified by the combination of port name and country.
As indicated by the VISIT Relation, a cruise includes visits to several ports, and a port is typically included in several cruises.
Both Passenger Number and Social Security Number are unique in the PASSENGER Relation. A particular person has a single Passenger Number that is used for all of the cruises that she takes.
The VOYAGE Relation indicates that a person can take many cruises and a cruise, of course, has many passengers.SHIP Relation
Ship Number
Ship Name
Ship Builder
Launch Date
GrossWeightCRUISE Relation
Cruise Number
Start Date
End Date
Cruise Director
Ship NumberPORT Relation
Port Name
Country
Number of Docks
Port ManagerVISIT Relation
Cruise Number
Port Name
Country
Arrival Date
Departure DatePASSENGER Relation
Passenger Number
Passenger Name
Social Security Number
Home Address
Telephone NumberVOYAGE Relation
Passenger Number
Cruise Number
Stateroom Number
FareAdditional step:
Using MySQL Workbench, create the relational data model for the database for happy cruise lines, which includes 6 tables. (Note: Be sure primary and foreign keys are correct). Export the PDF version of your model for submission.Then complete steps a – g.
Learn More
Note: On step g, provide correct SQL syntax for finding the result to each item i – viii. i.e. Do not use the informal relational approach – looking for valid, correct SQL as described in Chapter 4.
a. Identify the candidate keys of each relation.
b. Identify the primary key and any alternate keys of each relation.
c. How many foreign keys does each relation have?
d. Identify the foreign keys of each relation.
e. Indicate any instances in which a foreign key serves as part of the primary key of the relation in which it is a foreign key. Why does each of those relations require a multi-attribute primary key?
f. Identify the relations that support many-to-many relationships, the primary keys of those relations, and any intersection data.
g. Using the informal relational command language described in this chapter, write commands to:
Note: On step g, provide correct SQL syntax for finding the result to each item i – viii. i.e. Do not use the informal relational approach – looking for valid, correct SQL as described in Chapter 4.
i. Retrieve the record for passenger number 473942.
ii. Retrieve the record for the port of Nassau in the Bahamas.
iii. List all of the Ships built by General Shipbuilding, Inc.
iv. List the port name and number of docks of every port in Mexico.
v. List the name and number of every ship.
vi. Who was the cruise director on cruise number 38232.
vii. What was the gross weight of the ship used for cruise number 39482?
viii. List the home address of every passenger on cruise number 17543. -

GU CS371 Database Design Week 6 Assignment Chapter 7
$20.00GU CS371 Database Design Week 6 Assignment Chapter 7
Fundamentals of Database Management Systems 2nd Edition
Chapter 7 Questions
Exercise 2 – Using MySQL Workbench, recreate the data model given to you but in a “well-structured” format. Note: This essentially means adding foreign keys. Be sure to choose key names that make sense.
Minicase 1 - Using MySQL Workbench, recreate the data model given to you but in a “well-structured” format. Note: This essentially means adding foreign keys. Be sure to choose key names that make sense.Exercise:
2. Convert the Central Hospital entity-relationship diagram on the next page into a well-structured
relational database. (Instructions: Exercise 2 – Using MySQL Workbench, recreate the data model given to you but in a “well-structured” format. Note: This essentially means adding foreign keys. Be sure to choose key names that make sense.)Minicase:
Learn More
1. Happy Cruise Lines. Convert the Happy Cruise Lines entity-relationship diagram on the next page into a well structured relational database.
(Instructions: Minicase 1 - Using MySQL Workbench, recreate the data model given to you but in a “well-structured” format. Note: This essentially means adding foreign keys. Be sure to choose key names that make sense.) -

GU CS371 Database Design Week 7 Assignment Chapter 8 Final Project
$20.00GU CS371 Database Design Week 7 Assignment Chapter 8 Final Project
Fundamentals of Database Management Systems 2nd Edition
Questions and Task:
Question 1
In your own words discuss the benefits of normalization.Question 2
Do you think we should normalize our designs to higher levels than 3NF? Why or why not?Question 3
There are 14 physical database design techniques discussed in chapter 8. The goal of a quality physical design is to improve performance while disrupting the logical design as little as possible. Pick a technique, which you believe to be the most beneficial in accomplishing the above goal, and explain your reasoning.Question 4
Discuss the concept of an index and explain how they improve performance. Assignment "Final Project Overview" You just took a job with a University and have been asked to track some information about the courses they offer. The previous employee was using a spreadsheet to track this information. The University is expanding from three classes to three hundred classes. Enrollment is expected to increase from around 20 students to 5,000. Your supervisors are not very tech savvy and they simply ask you to continue maintaining the spreadsheet. Review the spreadsheet labeled final_project.xlsx.Explain the issues that exist with maintaining the data in its current form.
Learn More
Explain the process of migrating the data in its current form to a well formed data model by highlighting the following in detail:
Identify required attributes that need to be tracked
Identify functional dependencies Show the redesign in 1NF, 2NF, and 3NF (similar to figures 7.29, 7.31, 7.33)
Explain the benefits of the data in its new form.
Create the E-R diagram of your relational tables using MySQL Workbench.
Provide the SQL statement required to create at least one of your tables.
Provide the SQL statement required to delete at least one of your tables.
Provide the SQL statement required to create a view which includes Course #, Course Name, Time, and Days only.
Identify at least one index, which you believe would improve performance.
Explain your choice.
Propose some additional data items, which you believe may be beneficial to the University if tracked in your database (i.e. Descriptions, more info about the instructors and students, departments, etc).
Describe the steps required to implement these additions.
If you add a course description attribute to your course table, there may be some performance impacts imposed by the addition of this text field.
Discuss a physical design technique to improve the performance of the new course description field. -

ITCO333 Data Modeling and Design Unit 2 Individual Project
$20.00ITCO333 Data Modeling and Design Unit 2 Individual Project
Learn More
Deliverable Length: 1 Word document and 1 .accdb file
Details: Create a SQL Server database called: ITCO333Database. Using Data Definition Language (DDL) and Data Manipulation Language (DML) you will create the below DEPARTMENTS and EMPLOYEES tables. Before you begin creating the new tables, review your tables created in Unit 1 IP to ensure that your database is in third normal form (3NF).
Part 1:
Your ITCO333 database should contain data related to the organizational departments in your Unit 1 chosen topic. Therefore, create a DEPARTMENTS table with the following field specifications:
Field Name Data Type Other Comments and Requirements
Department_ID int Primary Key
Department_Name nvarcha(50)
Insert at least four records of sample data into the DEPARTMENTS table.
Your ITCO333 database should contain data related to employees in your Unit 1 chosen topic. Therefore, create an EMPLOYEES table with the following field specifications:
Field Name Data Type Other Comments and Requirements
Employee_ID Int Primary Key Last_Name nvarchar(50) Cannot be null.
First_Name nvarchar(50) Cannot be null.
Birth_Date datetime
Employment_Start_Date datetime
Hourly_Pay decia(p[,s]) Must be greater that 0
Department_ID Int Related to the DEPARTMENTS table.
Create a foreign key constraint.
Manager_ID Int Related to the Employee_ID in this table.
Create a foreign key constraint.
Insert at least eight records of sample data into the EMPLOYEES table.
Part 2: Using your Unit 1 ERD, create tables, fields, primary keys and relationship constraints in your ITCO333Database.
Insert your Unit 1 sample data into the newly created tables.
Part 3: Generate a SQL Server Database Diagram.
Additional Requirements: All tables must be in Third Normal Form (3NF). This may require you to normalize your Unit 1 data. Be sure to incorporate Instructor feedback from your Unit 1 IP. Use the following data types:
Integers: int
Decimals: decimal(p[,s])
Strings: nvarchar(50)
Date/Time: datetime
Deliverable: One Word document with:
SQL DDL to create database
SQL DDL to create tables (including EMPLOYEES and DEPARTMENTS tables)
SQL DML to insert data (including EMPLOYEES and DEPARTMENTS sample data)
SQL Server Database Diagram
The aforementioned SQL DML must be in text format (no screen shots). -
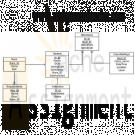
COM 330 Martial Arts R Us (MARU) ERD and Access Database
$20.00“Martial Arts R Us” (MARU) needs a database. MARU is a martial arts school with hundreds of students. It is necessary to keep track of all the different classes that are being offered, who is assigned to teach each class, and which students attend each class. Also, it is important to track the progress of each student as they advance.
Learn More
Create a complete Crow’s Foot ERD for these requirements:
• Students are given a student number when they join the school. This is stored along with their name, date of birth, and the date they joined the school.
• All instructors are also students, but clearly, not all students are instructors. In addition to the normal student information, for each instructor, the date that they start working as an instructor must be recorded, along with their instructor status (compensated or volunteer).
• An instructor may be assigned to teach any number of classes, but each class has one and only one assigned instructor. Some instructors, especially volunteer instructors, may not be assigned to any class.
• A class is offered for a specific level at a specific time, day of the week, and location. For example, one class taught on Mondays at 5:00 pm in Room #1 is an intermediate-level class. Another class taught on Mondays at 6:00 pm in Room #1 is a beginner-level class. A third class taught on Tuesdays at 5:00 pm in Room #2 is an advanced-level class.
• Students may attend any class of the appropriate level during each week so there is no expectation that any particular student will attend any particular class session. Therefore, the actual attendance of students at each individual class meeting must be tracked.
• A student will attend many different class meetings; and each class meeting is normally attended by many students. Some class meetings may have no students show up for that meeting. New students may not have attended any class meetings yet.
• At any given meeting of a class, instructors other than the assigned instructor may show up to help. Therefore, a given class meeting may have several instructors (a head instructor and many assistant instructors), but it will always have at least the one instructor that is assigned to that class. For each class meeting, the date that the class was taught and the instructors’ roles (head instructor or assistant instructor) need to be recorded. For example, Mr. Jones is assigned to teach the Monday, 5:00 pm, intermediate class in Room #1. During one particular meeting of that class, Mr. Jones was present as the head instructor and Ms. Chen came to help as an assistant instructor.
• Each student holds a rank in the martial arts. The rank name, belt color, and rank requirements are stored. Each rank will have numerous rank requirements. Each requirement is considered a requirement just for the rank at which the requirement is introduced. Every requirement is associated with a particular rank. All ranks except white belt have at least one requirement.
• A given rank may be held by many students. While it is customary to think of a student as having a single rank, it is necessary to track each student’s progress through the ranks. Therefore, every rank that a student attains is kept in the system. New students joining the school are automatically given a white belt rank. The date that a student is awarded each rank should be kept in the system. All ranks have at least one student that has achieved that rank at some time. -

Murachs SQL for SQL Server Chapter 10 How to create and maintain databases and tables with SQL statements
$12.00Murach’s SQL for SQL Server Chapter 10 How to create and maintain databases and tables with SQL statements
Learn More
Exercises
1. Create a new database named Membership.
2. Write the CREATE TABLE statements needed to implement the following design in the Membership database. Include reference constraints. Define IndividualID and GroupID with the IDENTITY keyword. Decide which columns should allow null values, if any, and explain your decisions. Define the Dues column with a default of zero and a check constraint to allow only positive values.
3. Write the CREATE INDEX statements to create a clustered index on the GroupID column and a nonclustered index on the IndividualID column of the GroupMembership table.
4. Write an ALTER TABLE statement that adds a new column, DuesPaid, to the Individuals table. Use the bit data type, disallow null values, and assign a default Boolean value of False.
5. Write an ALTER TABLE statement that adds two new check constraints to the Invoices table of the AP database. The first should allow (1) PaymentDate to be null only if PaymentTotal is zero and (2) PaymentDate to be not null only if PaymentTotal is greater than zero. The second constraint should prevent the sum of PaymentTotal and CreditTotal from being greater than InvoiceTotal.
6. Delete the GroupMembership table from the Membership database. Then write a CREATE TABLE statement that recreates the table, this time with a unique constraint that prevents an individual from being a member in the same group twice. -

CS362 Structured Query Language for Data Management Week 2 IP
$20.00CS362 Structured Query Language for Data Management Week 2 IP
Learn More
After creating the database schema, use Insert, Update, and Delete commands to populate the tables with the following information.
1. Insert the following classes' records:
Code Name Description
ACCT306 Accounting 1 This course introduces accounting concepts and explores the accounting environment. It covers the basic structure of accounting, how to maintain accounts, use account balances to prepare financial statements, and complete the accounting cycle. It also introduces the concept of internal control and how to account for assets.
CS362 Structured Query Language for Data Management This course gives complete coverage of SQL, with an emphasis on storage, retrieval, and manipulation of data.
ENG115 English Composition In this course, students focus on developing writing skills through practice and revision. Students will examine expository, critical, and persuasive essay techniques.
FIN322 Investments This course focuses on investments and investment strategies. Various investment vehicles such as stocks, bonds, and commodities are examined. Students will explore the principles of security analysis and valuation.
2. Insert the following advisors' records:
Name Email
Fred Stone fred@college.edu
Bob Gordon bob@college.edu
Jack Simpson jack@college.edu
3. Insert the following students' records:
Name Birthdate Gender StartDate GPA IsActive AdvisorID
Craig Franklin 1970-03-15 Male 2010-05-30 3.10 Yes 3
Harriet Smith 1982-04-15 Female 2010-05-30 3.22 Yes 1
George David 1984-11-05 Male 2010-10-01 0.00 Yes 3
Ben Jefferson 1976-09-25 Male 2009-02-21 1.80 No, the student has gone on temporary leave to pursue other opportunities but plans on returning in 1 year. 3
4. Delete the course named Investments from the system.
5. Change Harriet Smith’s birthdate to April 25, 1982 and her GPA to 3.25.
Copy and paste the work into your Key Assignment document and include screen shots of each step, describe what you did for each step and paste in the actual SQL text used to perform each step. Provide an introduction explaining the important of these commands in relation to your overall Key Assignment. -
CS362 Structured Query Language for Data Management Week 3 IP Select Statements
$20.00CS362 Structured Query Language for Data Management Week 3 IP Select Statements:
Learn More
Provide select statements to satisfy the following data requests:
1. List all active male students assigned to Advisors 1 or 3 (Fred Stone or Jack Simpson). (Where Clause - Filtering 3 different things: Active, Male Students, Adivsors)
2. Provide a list of all students without a biography. (focusing Null Biography)
3. What classes are in the English department? (Where Clause)
4. Create a list of all students and their advisors. Sort by the advisor’s name and then the student’s name. Include the student’s birth date, gender, and GPA. (join's statement combine the two tables students and class tables: Order by clause like birthday, gpa,etc)
5. How many students were born in the 1980s? (Aggregate using count expression)
6. Write a query to show the average GPA by gender. (Aggregate using count expression)
7. Provide a list of all advisors and the number of active students assigned to each. Filter out any advisors with more than 1 student. (Combine lines 4-6)
Copy and paste the work into your Key Assignment document and include screen shots of each step, describe what you did for each step and paste in the actual SQL text used to perform each step. Include an explanation as to how and where these queries or others like them can be used in your final system. Upload your document to the Submitted Tasks. -
CS362 Structured Query Language for Data Management Week 4 IP Extend the Design
$20.00CS362 Structured Query Language for Data Management Week 4 IP Extend the Design
Learn More
Using your Week 1 IP as a starting point, extend the design to accommodate degree programs. The new design should incorporate the following functionalities:
1. A degree has a name and description.
2. What degree is the student working towards? A student can only work on one degree at a time.
3. What classes are necessary to obtain a specific degree?
4. Provide the DDL script to add the tables for the new design changes. Include an updated diagram that shows all the tables in the system.
5. Write the DML script to insert 3 test records in each of the tables in the system. This data will be necessary to write the queries in the next assignment.
Copy and paste the work into your Key Assignment document and include screen shots of each step, describe what you did for each step and paste in the actual SQL text used to perform each step. Upload your document to the Submitted Tasks section.





