Search results for '/**/sElEcT * /**/fRoM MM_MOVIE;'
-
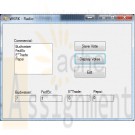
Clearly Visual Basic 2010 Chapter 10 Exercise 8 WKRK Solution
$15.00Clearly Visual Basic 2010 Chapter 10 Exercise 8 WKRK Solution
Each year, WKRK-Radio polls its audience to determine the best Super Bowl commercial. Th e choices are as follows: Budweiser, FedEx, E*Trade, and Pepsi. The station manager wants an application that allows him to enter a caller’s choice. The choice should be saved in a sequential access file. The application also should display the number of votes for each commercial. Create a Visual Basic Windows application. Use the following names for the solution, project, and form file, respectively: WKRK Solution, WKRK Project, and Main Form.vb. Create the interface shown in Figure 10-45, and then code the application. Save the solution and then start and test the application. Close the Code Editor window and then close the solution.
Learn More -
Microsoft Visual Basic 2010 Shelly Cashman Series Chapter 6 Case Problem 7 Factorial Math
$12.00Microsoft Visual Basic 2010 Shelly Cashman Series Chapter 6 Case Problem 7 Factorial Math
Create a requirements document and a Use Case Definition document, and design a Windows application based on the case project shown in Figure 6-134:
Most calculators have an operation called a “factorial” which is shown on a calculator key as an exclamation point. For example 5! (5 factorial) multiplies 5 * 4 * 3 * 2 * 1 to calculate the result of 120. Using loops to compute the factorial, display the following factorials in a Listbox object:
Learn More
1! 1
2! 2
3! 6
4! 24
5! 120
6! 720
7! 5040
8! 40320
9! -
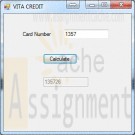
MS Visual Basic 2010 Diane Zak Chapter 10 Case Project Vita Credit
$12.00MS Visual Basic 2010 Diane Zak Chapter 10 Case Project Vita Credit
VITA CREDIT Each credit card number issued by Vita Credit contains five digits. The last digit is determined by multiplying the second and fourth digits by two and then adding the products to the first and third digits. The last digit in the sum is then appended to the first four digits. Create an application that allows the credit manager to enter four digits. The application should calculate the fifth digit and then display the card number.
Learn More
First four digits 1 3 5 7
STEP 1: CALC *2 *2 1 6 5 14
STEP 2: ADD 1 + 6 + 5+ 14 = 26
STEP 3: DISPLY 135726 -
CIS247A Week 5 Lab Composition Inheritance and Polymorphism
$15.00CIS247A Lab 5 Composition Inheritance and Polymorphism
Scenario and Summary
The objective of the lab is to take the UML Class diagram and enhance last week’s Employee class by making the following changes:
1. Create a derived class called Salaried that is derived from Employee.
2. Create a derived class called Hourly that is derived from Employee.
3. Create generalized input methods that accept any type of Employee or derived Employee object
4. Create generalized output methods that accept any type of Employee or derived Employee object
5. Override the base class CalculatePay method
6. Override one of the base class CalculateWeeklyPay methodsSTEP 1: Understand the UML Diagram
Analyze and understand the object UML diagram, which models the structure of the program.
• There are two new Employee derived classes (1) Salaried and (2) Hourly that are derived from the Employee class.
• The Employee class contains a new attribute employeeType and a new constructor that accepts as an argument the assigned employee type.
• Both the Salaried and the Hourly classes override only the CalculateWeeklyPay method of the Employee class (note, this is the method without any parameters.)
• The Salaried class has one attribute “managementLevel” that has possible values from MIN_MANAGEMENT_LEVEL to MAX_MANAGEMENT_LEVEL and a BONUS_PERCENT.
• The Salaried class has a default constructor and parameterized constructor that accepts all the general employee information plus the management level.
• The Hourly has a wage attribute, which respresents the hourly wage that ranges from MIN_WAGE to MAX_WAGE, a hours attributes, which represents the number of hours worked in a week that ranges from MIN_HOURS to MAX_Hours, and a category attributes that accepts string values.
• The Hourly class has a default constructor and parameterized constructor that accepts all the general employee information plus the hours and wage value.
• The Presentation Tier contains two new classes (1) The EmployeeInput class and the EmployeeOutput class
• The EmployeeInput class contains three static methods (1) CollectEmployeeInformation, which accepts any type of Employee object as a argument; (2) CollectHourlyInformation, which accepts only Hourly objects as an argument, and (3) CollectSalariedInformation, which accepts only Salaried objects as an argument.
• The EmployeeOutput class contains two methods (1) DisplayEmployeeInformation, which accepts any Employee type as an argument and (2) DisplayNumberObjects method.
• All the access specifers for the Employee attributes are changed to protected and are depicted with the “#” symbol.STEP 2: Create the Project
You will want to use the Week 4 project as the starting point for the lab. Use the directions from the previous weeks labs to create the project and the folders.
1. Create a new project named “CIS247_WK4_Lab_LASTNAME”. An empty project will then be created.
2. Delete the default Program.cs file that is created.
3. Add the Logic Tier, Presentation Tier, and Utilities folders to your proejct
4. Add the Week 4 project files to the appropraties folders.
5. Update the program information in the ApplicationUtilities.DisplayApplicationInformation method to reflect your name, current lab, and program description
Note: as an alternative you can open up the Week 4 project and make modifications to the existing project. Remember, there is a copy of your project in the zip file you submitted for grading.
Before attempting this week’s steps ensure that the Week 4 project is error free.STEP 3: Modify the Employee Class
1. Change the access specifier for all the private attributes to protected.
2. Add the new attribute employeeType, along with a “read only” property (that is only a “get” method) to access the employee type value.
3. Add a new constructor that only accepts the type attribute, which is then used to set the employeeType value. Also, this constructor should initialize all the default values. You can call the default constructor using the syntax: public Employee(string employeeType) : this() { }
4. Modify the parameterized constructor that accepts the employee information to accept the employee type, and then set the employeeType with this value.
5. Modify the ToString Method to include the employee type.STEP 4: Create the Salaried Class
1. Using the UML Diagrams, create the Salaried class, ensuring to specify that the Salary class inherits from the Employee class.
2. For each of the constructors listed in the Salaried class ensure to invoke the appropriate super class constructor and pass the correct arguments to the super class constructor.
3. Override the CalculateWeeklyPay method to add a 10 percent bonus to the annualSalary depending on the management level. The bonus percent is a fixed 10 percent, and should be implemented as a constant. However, depending on the management level the actual bonus percentage fluctuates (i.e., actualBonusPercentage = managementLevel * BONUS_PERCENT).
4. Override the ToString method to add the management level to the employee information.STEP 5: Create the Hourly Class
1. Using the UML Diagrams, create the Hourly classes, ensuring to specify that the Hourly class inherits from the Employee class.
2. For each of the constructors listed in the Hourly class ensure to invoke the appropriate super class constructor and pass the correct arguments to the super class constructor. Notice, that the Hourly employee DOES NOT have an annual salary, which we will then have to calculate (see below).
3. Create a Category property (get/set) and the valid category types are “temporary”, “part time”, “full time”.
4. Create a Hours property (get/set) for the hours attributes and validate the input using the constants shown in the UML diagram, but since an Hourly employee does not have a formal annual salary we will need to calculate this each time the hour (and wage) properties are set. Add the following code after the validation code in the hours property: base.AnnualSalary = CalculateWeeklyPay() * 48; (assumes working 48 weeks a year).
5. Create an Wage property (get/set) for the wage attributes and validate the input using the constants shown in the UML diagram. Add the following code after the validation code in the wage property: base.AnnualSalary = CalculateWeeklyPay() * 48; (assumes working 48 weeks a year)
6. Override the CalculateWeeklyPay method by multiplying the wages by the number of hours.
7. Update the ToString method to add the category, hours, and wages to the hourly employee information.STEP 6: Create the EmployeeInput Class
1. Create a new class in the Presentation Tier folder called “EmployeeInput”
2. Create a static void method called CollectEmployeeInformation that has a single Employee parameter. The declaration should look something like the following:
public static void CollectEmployeeInformation(Employee theEmployee)
3. Write code statements similiar to what you created in the Week 4 project to collect the generic employee information from the user, except instead of using specific employee objects use the “theEmployee” parameters. For example:
In Week 4, you had something like:
employee1.FirstName = InputUtilities.GetStringInputValue(“First name”);
In the CollectionEmployeeInformation method this can be translated to the following;
theEmployee.FirstName = InputUtilities.GetStringInputValue(“First name”);
4. Write statements to collect all the generic employee information, including the Benefits information, as you did in the Week 4 project. However, since not all derived types have a AnnualSalary value, DO NOT collect the annual salary data.
5. Create a new static void method called CollectEmployeeInformation that accepts an Hourly employee object. Using the InputUtilities methods write statements to collect the wage and hours from the user.
6. Create a new static void method called CollectSalariedInformation that accepts a Salaried employee object. Using the InputUtilties methods write statements to collect the management level and the annual salary.STEP 7: Create the Main Program
1. Create an array of type Employee that will hold three employee objects. Create three new objects, one Employee, one Hourly and one Salaried in positions 0, 1 and 2 of the array respectively. Make sure to use the constructors the accept the employee type and provide appropriate values for the employee type (e.g. “Generic”, “Hourly”, “Salaried”).
2. Using a FOR loop iterate through the array and collect all the generic employee information, using the EmployeeInput.CollectEmployeeInformation method.
3. If the current item in the array is an Hourly object, then use the EmployeeInput.CollectHourlyInformation method to collect the hourly information.
4. If the current item in the array is a Salaried object, then use the EmployeeInput.CollectSalariedInformation method to collect the salaried information.
Use the following if statement to determine the specific type of object:
if (employeeList[i] is Hourly)
EmployeeInput.CollectHourlyInformation((Hourly)employeeList[i]);
else if (employeeList[i] is Salaried)
EmployeeInput.CollectSalariedInformation((Salaried)employeeList[i]);
5. After the information has been collected display the employee information using the EmployeeOutput.DisplayEmployeeInformation method.
6. Before terminating the program display the number of employee objects that have been created.STEP 8: Compile and Test
When done, compile and run your program.
Then debug any errors until your code is error-free.
Check your output to ensure that you have the desired output and modify your code as necessary and rebuild.
The output of your program should resemble the following:On-screen output display:
Welcome the Employee Hierarchy Program
CIS247, Week 5 Lab
Name: SolutionThis program tests an Employee inheritance hierarchy
Learn More
*********************** Display Employee’s Data **********************
Employee Type GENERIC
First Name John
Last Name Student
Gender Male
Dependents 3
Annual Salary $20,000.00
Weekly Pay $384
Health Insurance Blue Cross
Life Insurance $20,000
Vacation 21
*********************** Display Employee’s Data **********************
Employee Type Hourly
First Name Mary
Last Name Noia
Dependents 4
Annual Salary $100,000
Weekly Pay $2,080.00
Health Insurance Blue Cross
Life Insurance $175,000
Vacation 24
Hours 40
Wage 52
Category Full Time
*********************** Display Employee’s Data **********************
Employee Type Salaried
First Name Sue
Last Name Smith
Gender Female
Dependents 2
Annual Salary $100,000.00
Weekly Pay $2,500.00
Health Insurance Blue Cross
Life Insurance $300,000
Vacation 15
Level 3
total Number of Employess in Database: 3 -
CIS247A Week 7 Lab The Abstract Racer Inheritance Hierarchy Program
$15.00CIS247A Week 7 Lab The Abstract Racer Inheritance Hierarchy Program
Scenario and Summary
This week, you will be implementing inheritance by creating a generic Racer base class along with two derived classes called StreetTuner and HotRod. You will make the Racer class abstract and include the abstract method IsDead() in the Racer class.STEP 1: Understand the UML Diagram
The UML diagram four classes defined (1) Racer, (2) Engine, (3) Hot Rod, and (4) StreetTuner classes.The Racer class is the base parent abstract class of the Hot Rod and Street Tuner classes, which is represented by a directed line from the Hot Rod and Street Tuner classes to the Racer class and the end of the line touching the Racer class is a broad, unfilled arrow head. The racer class contains a engine object, which is represented by a directed line from the engine class to the Racer class, with a filled diamond touching the racer class, this line is labeled as a 1 to 1 relationship meaning that each racer object will contain one engine object and each engine is related to a single racer object.
The class's attributes and methods are defined in separate class diagrams, and each class diagram is represented by a rectangular box subdivided into three vertically separated rectangular sub-sections. The top section contains the class name, the middle section contains the class attributes, and the bottom section contains the class methods.
STEP 2: Build the Inheritance Hierarchy
1. Create a project called "CIS247_WK7_Lab_LASTNAME".
2. Build the class structure shown in the UML diagram. Remember to include properties for each class attribute.STEP 3: Implement the Logic for the HotRod Class
1. Provide suitable logic for the ToString method. As always, the ToString method should reveal the state of an object.
2. For the IsDead() method in HotRod, use the logic to implement the base class abstract IsDead method.
Hint: To generate a random number, use the following code, which returns a random number from 0 to 1:
Random rnd = new Random();
rnd.NextDouble();
Pseudocode for the IsDead method of HotRod
Random rnd = new Random();
boolean deadif (speed > 50 && rnd.NextDouble() > 0.6)
if (engineHorsePower < 300 && blower=true)
dead = false
else
dead = true
end if
else if (speed > 100 && rnd.NextDouble() > 0.4)
if (engineHorsePower >= 300 && blower = true)
dead = true
else
dead = false
end if
else
dead = false
end ifSTEP 4: Implement the logic for the StreetTurner class
1. Provide suitable logic for the ToString method. As always, the ToString method should reveal the state of an object.
2. For the IsDead method in StreetTurner, use the logic below to implement the inherited abstract base class method called IsDead.
Pseudocode for the IsDead method of StreetTuner
Random rnd = new Random();
boolean dead
if (speed > 50 && rnd.NextDouble() > 0.6)
if (engineHorsePower < 300 && nitrous=true)
dead = false
else
dead = true
end if
else if (speed > 100 && rnd.NextDouble() > 0.4)
if (engineHorsePower >= 300 && nitrous = true)
dead = true
else
dead = false
end if
else
dead = false
end ifSTEP5: Construct the Main Program
1. Create an array of Racer objects that will hold two Racer objects.
2. Write a method called CollectRacerInformation that accepts as an argument a Racer object, and then prompts the user to provide the following information for each racer:
a. Racer name;
b. Racer Speed;
c. Number of cylinders in the racer's engine;
d. Horsepower of the racer's engine; and
e. Nitrus or blower option, depending on the type of Racer object.
[Hint: In order to be able to collect all information for the derived classes as well, consider creating a base class method called ReadRacerData in the Racer class, which you will then override in the derived classes to capture the required info per class. Call the ReadRacerData method within the CollectRacerInformation method.]
3. Write a method called "DisplayRacerInformation" that accepts as an argument a Racer object, and then displays all of the information for the specific racer type.
4. Create a racer object of each type, and invoke the CollectRacerInformation passing in the Racer object. Then, store each object in the array.
5. Iterate through the Racer array list and, for each Racer, display all of the Racer's attribute information (call the DisplayRacerInformation method for each object). Don’t forget to indicate whether or not the Racer is dead!STEP 6: Compile and Test
Learn More
When done, compile and run your program.
Then, debug any errors until your code is error-free.
Check your output to ensure that you have the desired output and modify your code as necessary and rebuild. Your code may resemble the following:
Welcome the Abstract RAcer Inheritance Hierarchy Program
CIS247, Week 7 Lab
Name: Solution
This Program test an Anstract Racer Inheritance hierarchy
**************** Collecting Racer's Basic Data ****************
Enter racer's name: Fast One
Enter racer's speed: 345
Enter number of cylinders in racer's engine: 20
Enter horsepower of racer's engine: 250
Enter nitrus option (Y/N): Y
**************** Collecting Racer's Basic Data ****************
Enter racer's name: Lightning
Enter racer's speed: 380
Enter number of cylinders in racer's engine: 16
Enter horsepower or racer's engine: 275
Enter blower option (Y/N): Y
**************** Display Racer's Data ****************
Racer's Name : Fast One
Racer's Speed : 345
Engine Cylinders : 20
Engine Horsepower : 250
Racer's Type : STREET TUNER
With Nitrus Option : Yes
Still Working? : Yes!
**************** Display Racer's Data ****************
Racer's Name : Lightning
Racer's Speed : 380
Engine Cylinders : 16
Engine Horsepower : 275
Racer's Type : HOT ROD
With Nitrus Option : Yes
Still Working? : Yes!
Thank you for using the Abstract Racer Inheritance Hierarchy -

CMIS 320 Lab 2 Homework 2 Data modeling and Sample database
$15.00CMIS 320 Lab 2 Homework 2 Data modeling and Sample database
Homework Submission Requirements:
Homework should be submitted as an attached file in your assignment folder. text for coding and result of execution and MS Word format for documenting are preferred. Data modeling diagram could be copied and pasted into a Word doc.
You must name your file to include your first initial of your first name and last name.
Part I is 4 points and Part II is 1 points. Total is 5. Quiz is not required for grading.Part I Data Modeling
For each of the following descriptions:
a. A piano manufacturer wants to track all pianos it makes. Each piano has a unique serial number and a manufacturing completion date. Each instrument represents exactly one piano model, all of which have an identification number and model. The company produces thousands of pianos of a certain model, and the design is specified before any single piano exists.
b. A vendor builds multiple types of tablet computers. Each has a type identification number and a name. The key specifications for each type include amount of storage and display type. The company uses multiple processor types, exactly one of which is used for a specific tablet type. The same processor can be used in multiple types of tablets. Each processor has a manufacturer and a manufacturer's unique code that identifies it.
perform the following tasks:
1. Identify the degree and cardinalities of the relationship.
2. Express the relationships graphically with an E-R diagram.
Document your work into a single, well-organized, well-written word document and submit no later than due date.Part II Lab 2
In lab 2, you will learn how to run a SQL script to create a sample database in your schema in NOVA Oracle database. You also start to learn simple SQL commands, such as select and insertClick here to open Lab 2 instruction page
This part of lab is to learn to run a SQL script on NOVA Oracle database server, and spool screen output to a text file. These techniques will be used when you work on your project 1 and 2. Download script file. This is sql script file containing completed sql commands to create tables and constraints and populate data to each table. The database you create is called JustLee Book Store. The code should be bug free.
Learn More
Download lab2.sql script
Start spool command and run the script:
Log on NOVA, make a dir named scripts using command mkdir scripts
Then cd to newly created script directory
Upload your script to scripts directory using FTP
(I downloaded a free FTP client CORE FTP LE) and use it to upload and download file)
Now you have a newly create dir and your script is uploaded. You are ready to run your script.
Using SQL*Plus, log on NOVA Oracle database with your account
At SQL prompt,Type the following command to turn on spool function: SQL>spool spool01.lst
spool01.lst is the spool file name
Then use this command to run the script: SQL>@lab2.sql
The command will execute all the SQL commands inside the script and output will be spooled to spool01.lst
In the script, there are drop table statement as well. When first run, these commands will fail because the tables are not created yet.
You can run the script multiple times without any problems.
When you finish the execution, issue command SQL>spool off
This command will end spool function and save output to the file you defined
When you have done all of these. Use FTP get spool01.lst to your local computer and submit it as part of homework 2
You should know how to perform the following tasks using sqlplus on NOVA Oracle database after you complete this lab:
Using FTP to upload or download a file (scripts...)
Using sqlplus to log on to NOVA Oracle database
Using sqlplus command, spool to output screen output to a text file and transfer the file back to your local PC.
Understand the steps taken place when you perform FTP file transfer and Spooling your output.
Test the database you create and learn SQL queries.
You need to spool the execution results of the following commands.
Do a database query: select table_name from user_tables; USER_TABLES is a database system view that allow users to see the tables they created in their own schema.
You should be able to list the tables you just created
use this query: select * from "table_name from the above query"; you can retrieve the data in these tables one a time
use this query: select count(*) from "table_name from the above query"; you can retrieve the record counts in these tables one a time
Use SQL*Plus command "desc books" to check columns and their datatypes. And insert one record into the table. Use SQL command "commit" to save the record into your database.
When you have done all of these. Use FTP get spooled file to your local computer and submit it as part of homework 2 -
BMIS 208 Programming Assignment 3 Analyze Mortgage
$15.00BMIS 208 Programming Assignment 3 Analyze Mortgage
Adapted from Introduction to Programming Using Visual Basic 2012, 9/E, David I. Schneider
Create a Visual Basic program to analyze a mortgage. The user should enter the amount of the loan, the annual percentage rate of interest, and the duration of the loan in months. When the user clicks on the button, the information that was entered should be checked to make sure it is reasonable. If bad data have been supplied, the user should be so advised. Otherwise, the monthly payment and the total amount of interest paid should be displayed. The formula for the monthly payment is:
Learn More
Payment = p * r / (1 – (1 + r) ^ (-n)),
Where p is the amount of the loan, r is the monthly interest rate (annual rate divided by 12) given as a number between 0 ( for 0 percent) and 1 (for 100 percent), and n is the duration of the loan in months.The formula for the total interest paid is:
total interest = n * payment – p.
1. Design your screen to look like the one below.
2. Store the amounts entered by the user in variables and use these variables in the formula.
3. Use appropriate naming conventions for controls and variables.
4. Include internal documentation to describe the logic in your program (i.e. put comments in your code).
5. Make sure your error messages are meaningful.
6. Ensure that the user cannot enter anything into controls that display your totals. -
CIS407 Lab 3 Week 3 User activity monitoring ASP.NET Web Application
$12.00This course has expired to download the latest version of CIS407A Labs click here
CIS 407 iLab 3 of 7: User activity monitoring
iLAB OVERVIEW
Scenario/Summary
In this lab, we will demonstrate how to save user activity data in a database. We will be creating a new form to display the user activity data, a new dataset to contain the data, a data access class to structure the code, and a function within the data access class to save users' activity data when users visit the Personnel form page (frmPersonnel.aspx). We will also be adding server side validation to the frmPersonnel for you added in the previous lab and update or main menu for the new functionality. INCLUDE A SCREENSHOT OF THE ASSIGNMENT SUCCESSFULLY RUNNING TO RECEIVE CREDITDeliverables
All files are located in the subdirectory of the project. The project should function as specified: When you visit the Personnel form page (frmPersonnel.aspx), a record should be saved in the tblUserActivity table with the IP address, form name accessed (frmPersonnel), and the date accessed. When you click the "View Activity" button, you should see at least one record with this information. When the user goes to the frmPersonnel web form and enters data the following business rules are to be enforced:
• Fields may not be empty or filled with spaces. If any field is empty, turn that field background color to yellow and add to/create an error message to be shown in the error label.
• The end date must be greater than the start date. If the end date is less than the start date turn both date fields yellow and add to/create an error message to be shown in the error label.
If all fields validate properly, then the session state items should be set properly and the user should see the frmPersonnelVerified form with all the values displayed. You will also add a new item to frmMain that will take the user to the new frmUserActivity form you added. Add the proper link and a hyperlinked image to allow the user to select this new option. Once you have verified that everything works, save your website, zip up all files, and submit in the Dropbox.iLAB STEPS
STEP 1: Data Connection, Dataset and Data Access Class (10 points)
1. Open Microsoft Visual Studio.NET 2008.
2. Open the PayrollSystem website by clicking on it in the Recent Projects list, or by pulling down the File menu, selecting Open Website, navigating to the folder where you previously saved the PayrollSystem, and clicking Open.
3. Download the PayrollSystem_DB.MDB file from Doc Sharing and save it on your local computer. (Note: your operating system may lock or block the file. Once you have copied it locally, right click on the file and select Properties and then Unblock if available). Then add it to the PayrollSystem website as follows: In Visual Studio, in the Solution Explorer click Website, Add Existing Item, then navigate to the PayrollSystem_DB.MDB file you downloaded and click the Add button.
4. Now we need to create a new connection to the PayrollSystem_DB.MDB. To begin, click View Server Explorer.
5. When the Server Explorer toolbox appears, click the Connect to Database button.
6.When the Add Connection dialog appears, click the Change button. In the "Change Data Source" dialog, select MS Access Database File; Uncheck Always use this Selection; then click OK.
7. Click the Browse button to navigate to the PayrollSystem_DB.mdb file in your website folder, then click "Open". (NOTE: Be sure you select the PayrollSystem_DB.mdb file in your PayrollSystem website folder, not the one you originally downloaded from Doc Sharing!) Click Test Connection. You should receive a message that the test connection succeeded. Click OK to acknowledge the message, then click "OK" again to close the Add Connection dialog.
8. The PayrollSystem_DB.mdb should be added to the Server Explorer. Expand the database, then expand the Tables entry under the database until you see tblUserActivity. Leave the Server Explorer window open for now as you will be returning to it in a moment.
9. Create a new dataset by selecting Website Add New Item. Under Templates, select the Dataset item. Enter dsUserActivity.xsd for the name. Click Add.
10. Click here for text discription of this image.
11. If the following message appears, select Yes. You want to make this dataset available to your entire website.
12. If the TableAdapter Configuration Wizard dialog appears, click Cancel. (We will be configuring a Data Adapter for this dataset later in C# code, so we do not need to run this wizard.)
13. Drag-and-drop the tblUserActivity table from the Server Explorer window into the dsUserActivity dataset in the editor window.
NOTE: If you see a message that says your connection uses a local data file that is not in the current project, that indicates you did not select the correct PayrollSystem_DB.mdb file when you created your data connection. To fix this problem, click No, then right-click on PayrollSystem_DB.mdb in the Server Explorer window and choose Modify Connection. Click the Browse button, navigate to the PayrollSystem_DB.mdb file that is in your PayrollSystem website folder, and click Open. Test the connection, then click OK.
14. Click the Save icon on the toolbar to save the dsUserActivity.xsd dataset.
15. Click here for text discription of this image.
16. (You can now close the Server Explorer window if you wish.)
17. Create a new class to contain the C# code that will access this dataset. To do so, click Website, Add New Item. In the Add New Item dialog, select the Class template, and enter clsDataLayer for the name. Make sure the Language is set to Visual C#. Click "Add".
18. Click here for text discription of this image.
19. If the following message appears, select Yes. You want to make this class available to everything in your solution.
20. Add the following to the top of your class, below any other using statements created for you by Visual Studio:
// Add your comments here
using System.Data.OleDb;
using System.Net;
using System.Data;
21. Add the following three functions inside the squiggly braces for the "public class clsDataLayer" class, above the beginning of the "public clsDataLayer()" constructor:
// This function gets the user activity from the tblUserActivity
public static dsUserActivity GetUserActivity(string Database)
{
// Add your comments here
dsUserActivity DS;
OleDbConnection sqlConn;
OleDbDataAdapter sqlDA;
// Add your comments here
sqlConn = new OleDbConnection("PROVIDER=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" +
"Data Source=" + Database);
// Add your comments here
sqlDA = new OleDbDataAdapter("select * from tblUserActivity", sqlConn);
// Add your comments here
DS = new dsUserActivity();
// Add your comments here
sqlDA.Fill(DS.tblUserActivity);
// Add your comments here
return DS;
}
// This function saves the user activity
public static void SaveUserActivity(string Database, string FormAccessed)
{
// Add your comments here
OleDbConnection conn = new OleDbConnection("PROVIDER=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" +
"Data Source=" + Database);
conn.Open();
OleDbCommand command = conn.CreateCommand();
string strSQL;
strSQL = "Insert into tblUserActivity (UserIP, FormAccessed) values ('" +
GetIP4Address() + "', '" + FormAccessed + "')";
command.CommandType = CommandType.Text;
command.CommandText = strSQL;
command.ExecuteNonQuery();
conn.Close();
}
// This function gets the IP Address
public static string GetIP4Address()
{
string IP4Address = string.Empty ;
foreach (IPAddress IPA in
Dns.GetHostAddresses(HttpContext.Current.Request.UserHostAddress)) {
if (IPA.AddressFamily.ToString() == "InterNetwork") {
IP4Address = IPA.ToString();
break;
}
}
if (IP4Address != string.Empty) {
return IP4Address;
}
foreach (IPAddress IPA in Dns.GetHostAddresses(Dns.GetHostName())) {
if (IPA.AddressFamily.ToString() == "InterNetwork") {
IP4Address = IPA.ToString();
break;
}
}
return IP4Address;
}STEP 2: frmUserActivity, frmPersonnel, frmMain (10 points)
18. Create a new Web form called frmUserActivity. Switch to Design Mode and add a Label and GridView (found under the Toolbox, Data tab) having the following properties:
Property Value
Label - Text User Activity
GridView - (ID) grdUserActivity
19. Go to the Page_Load method and add the following code:
if (!Page.IsPostBack) {
// Declares the DataSet
dsUserActivity myDataSet = new dsUserActivity();
// Fill the dataset with what is returned from the function
myDataSet = clsDataLayer.GetUserActivity(Server.MapPath("PayrollSystem_DB.mdb"));
// Sets the DataGrid to the DataSource based on the table
grdUserActivity.DataSource = myDataSet.Tables["tblUserActivity"];
// Binds the DataGrid
grdUserActivity.DataBind();
}
20. Open the frmMain form, add a new link button and image button to point to the new frmUserActivity. Find an image to use for the image button and add the new option as View User Activity.
21. Go to the frmMain Page_Load and add the following code:
// Add your comments here
clsDataLayer.SaveUserActivity(Server.MapPath("PayrollSystem_DB.mdb"), "frmPersonnel");
22. On the frmUserActivity form, add the CoolBiz logo hyperlinked logo at the top of the page so that when clicked the user is returned to frmMain.
23. In the Solution Explorer, right click on the frmMain.aspx form and select Set As Start Page. Run your project. When you open the project, a record should be saved in the tblUserActivity table with the IP address, form name accessed (frmPersonnel), and the date accessed. When you click the View Activity button, you should see at least one record with this information.
24. You will now add server side validation code to the frmPersonnel page. Currently, when the Submit button is pressed, the frmPersonnelVerified page is displayed. This is because the frmPersonnelVerified page is set as the Submit button's PostBackUrl property. Instead of having the page go directly to the frmPersonnelVerified page when the Submit button is pressed, we want to do some server side validation. If any of the validation rules fail, we will redisplay the frmPersonnel page with the fields in question highlighted in yellow with an error message displayed.
First, it is important to understand what is currently happening when the submit button is pressed. This is causing a postback of the form to the frmPersonnelVerified form. When this postback happens, all of the data in the fields on the frmPersonnel form are sent to the frmPersonnelVerified form as name value pairs. In the Page_Load code of frmPersonnelVerified these values are picked up from the Request object and displayed. Each name value pair will be in the Request object as the ID of the control containing the value and the value itself. We can pass data between pages by using Session state instead. In order to do validation on the values but still have the values visible on the frmPersonnelVerified page, we will need to change not only the PostBack URL of the frmPersonnel page but also how the frmPersonnelVerified form is getting the data – it will need to get it from Session state rather than from the Request object.
Make the following changes:
1. Clear the Submit button PostBackURLProperty on the frmPersonnel form.
2. In the btnSubmit_Click event handler get each value from the data entry fields and set Session state items for each.
3. Change the frmPersonnelVerified code behind to get the values from the Session state items you created in the previous step.
When you are done with these steps, you should be able to enter data on the frmPersonnel data entry form and then click the Submit button. The frmPersonnelVerified page should then be displayed with the values that were in the data entry fields on frmPersonnel.
Make sure this is all working before proceeding to the next steps.
25. Add a label to the frmPersonnel form with an ID of lblError. Do not place the label to the right or left of any of the controls on the form. Add it below the controls or above the controls. The text property of this label should be set to an empty string.
26. Add code to perform server side validation in response to the submit button being clicked. Here are the business rules we want to enforce (remember this will be server C# code in the frmPersonnel code behind): Fields may not be empty or filled with spaces. If any field is empty, turn that field background color to yellow and add to/create an error message to be shown in the error label. The end date must be greater than the start date. If the end date is less than the start date, turn both date fields yellow and add to/create an error message to be shown in the error label. If all fields validate properly then the session state items should be set properly and the user should see the frmPersonnelVerified form with all the values displayed.
27. Lab Hints: To set a value in session state do the following:
Session["txtFirstName"] = txtFirstName.Text;
28. "txtFirstName" is the key and txtFirstName.Text is the value.
29. To get this same value back from the session we use the key and the Session object as follows:
Session["txtLastName"].ToString()
30. There is a Trim method on the string object that will automatically remove spaces from the beginning and end of a string. Remember, you can turn an object like a Session item object into a string using the Convert class or just using it's ToString() method.
31. You may want to create variables to work with for validation rather than using the Request item objects directly.
32. To turn a string into a DateTime object you can use the DateTime method Parse. If you had a date value stored in a string called strDate, you could turn it into a DateTime object like this:
DateTime myDateTimeObject = DateTime.Parse(strDate);
33. You can compare two DateTime objects by using the DateTime.Compare method. If you had two DateTime objects called dt1 and dt2 you can check to see if dt1 is greater than dt2 by doing this:
if (DateTime.Compare(dt1,dt2) > 0)
34. DateTime.Compare will return a 0 if the two dates are equal, a 1 if dt1 is greater than dt2, and a -1 if dt1 is less than dt2.
35. If you put in an invalid date for either of the date fields, you will get an exception/server error when trying to parse the values. We will address this in a later lab – for now make sure you enter valid dates (valid meaning a date in the form of mm/dd/yyyy).
36. If I had a TextBox control that was called txtAge and you wanted to set it's background color you could do this:
txtAge.BackColor = System.Drawing.Color.Yellow;
37. Remember to clear the PostBackURL property of the submit button!STEP 3: Verify and submit (10 points)
28. View the video above on what functions your lab should have so far.
29. Run your project. When you open the project, and go to the main menu form a record should be saved in the tblUserActivity table with the IP address, form name accessed (frmPersonnel), and the date accessed. When you click the View Activity button you should see at least one record with this information. The validation and error display should work for entering data. All navigation and hyperlinks should work.
Once you have verified that it works, save your project, zip up all files, and submit in the Dropbox.NOTE: Make sure you include comments in the code provided where specified (where the " //Your comments here" is mentioned) and for any code you write, or else a five point deduction per item (form, class, function) will be made. You basically put two forward slashes, which start the comment; anything after the // on that line is disregarded by the compiler. Then type a brief statement describing what is happening in following code. Comments show professionalism and are a must in systems. As a professional developer, comments will set you apart from others and make your life much easier if maintenance and debugging are needed.
Learn More -
CIS407 Lab 4 Week 4 Web forms with database interaction ASP.NET Web Application
$12.00This course has expired to download the latest version of CIS407A Labs click here
CIS 407 iLab 4 of 7: Web forms with database interaction
iLAB OVERVIEW
Scenario/Summary
In this lab, we will start with the form we created in Week 2 (frmPersonnel) and add functionality to INSERT records into a database table and SELECT records for display to the user. We will create a typed dataset, a Data Layer class, several functions to access the data, and a connection to a database. We also will add a search form to allow the user to search records in the database and display the results of that search.
Instructions for Week 4 iLab: Web Forms with Database InteractionDeliverables
All files are located in the subdirectory of the project. The project should function as specified: When you press the Submit button in frmPersonnel, a record should be saved in the tblPersonnel table having the FirstName, LastName, PayRate, StartDate, and EndDate you entered on the form. Add a search feature to the project. Update your main navigation page with the new options. Once you have verified that it works, save your website, zip up all files, and submit it in the Dropbox.iLAB STEPS
STEP 1: Data Layer (10 points)
1. Open Microsoft Visual Studio.NET 2008.
2. Click the ASP.NET project called PayrollSystem to open it.
3. Open the clsDataLayer class and add the following function:
// This function saves the personnel data
public static bool SavePersonnel(string Database, string FirstName, string LastName,
string PayRate, string StartDate, string EndDate)
{
bool recordSaved;
try {
// Add your comments here
OleDbConnection conn = new OleDbConnection("PROVIDER=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" +
"Data Source=" + Database);
conn.Open();
OleDbCommand command = conn.CreateCommand();
string strSQL;
// Add your comments here
strSQL = "Insert into tblPersonnel " +
"(FirstName, LastName, PayRate, StartDate, EndDate) values ('" +
FirstName + "', '" + LastName + "', " + PayRate + ", '" + StartDate +
"', '" + EndDate + "')";
// Add your comments here
command.CommandType = CommandType.Text;
command.CommandText = strSQL;
// Add your comments here
command.ExecuteNonQuery();
// Add your comments here
conn.Close();
recordSaved = true;
} catch (Exception ex) {
recordSaved = false;
}
return recordSaved; }
4. In the frmPersonnelVerified form, go to the Page_Load() event and add the following code after the existing code (but in the Page_Load event handler):
// Add your comments here
if (clsDataLayer.SavePersonnel(Server.MapPath("PayrollSystem_DB.mdb"),
Session["txtFirstName"].ToString(),
Session ["txtLastName"].ToString(),
Session ["txtPayRate"].ToString(),
Session ["txtStartDate"].ToString(),
Session ["txtEndDate"].ToString()))
{
txtVerifiedInfo.Text = txtVerifiedInfo.Text +
"\nThe information was successfully saved!";
}
else
{
txtVerifiedInfo.Text = txtVerifiedInfo.Text +
"\nThe information was NOT saved.";
5. Add comments for all code containing // Add your comments here.
6. Test your work to make sure no errors occur! (Make sure to put in valid date values for the date data entry fields).STEP 2: Data Display and Search (10 points)
7. Using the skills you learned in Week 3, create a new DataSet for the tblPersonnel table (called the DataSet dsPersonnel).
8. Using the skills you learned in Week 3, create a new function called GetPersonnel in the clsDataLayer class. This function should retrieve all data from the tblPersonnel table and return it in the form of a dsPersonnel DataSet. Use the GetUserActivity function as an example.
9. Create a new Web form called frmViewPersonnel.
10. Using the skills you learned in Week 3, add a GridView control (called grdViewPersonnel) to the form. This GridView control will be used to display data from the tblPersonnel table. Add the CoolBiz logo at the top of the page and make sure it links back to frmMain.
11. Add the following code to the Page_Load() function in frmViewPersonnel:
if (!Page.IsPostBack) {
// Declare the DataSet
dsPersonnel myDataSet = new dsPersonnel();
// Fill the dataset with what is returned from the function
myDataSet = clsDataLayer.GetPersonnel(Server.MapPath("PayrollSystem_DB.mdb"));
// Set the DataGrid to the DataSource based on the table
grdViewPersonnel.DataSource = myDataSet.Tables["tblPersonnel"];
// Bind the DataGrid
grdViewPersonnel.DataBind();
}
12. Return to the frmPersonnel Web form and add a button ((ID) = btnViewPersonnel, Text = View Personnel) which, when clicked, will display form frmViewPersonnel.
13. Using the skills you learned in Week 3, open the frmPersonnelVerified form and add a button ((ID) = btnViewPersonnel, Text = View Personnel) which, when clicked, will display form frmViewPersonnel. NOTE: This is the same button with the same functionality that you added to form frmPersonnel in the previous step. Also add a new link and linked image to frmMain called View Personnel that will go to the new frmViewPersonnel page you created.
14. You will now add a search feature to allow the user to find and display data. The user will enter a last name and the web application will display the grid of employees with all employees that match that last name.
15. Create a new web form called frmSearchPersonnel. Add the hyperlinked Cool Biz logo to this page. Also add a new item on frmMain (with a link button and image button) called Search Personnel.
16. On the frmSearchPersonnel form, add a label that displays "Search for employee by last name:". Next to the label, add a text box with an ID of txtSearchName. Add a button with an ID of btnSearch and set the text of the button to "Search".
17. When the frmSearchPersonnel Search button is pressed, the frmViewPersonnel is displayed. At this point, no searching is actually happening, but you have the forms you need and the navigation working. Now you can focus on the coding you will need to do to have the grid only display matching employees.
18. Before calling the GetPersonnel method you added previously in the lab, get the value that is in the Request["txtSearch"] item. When the form posts the search page results to the frmViewPersonnel, the name value pair for the search value is passed as part of the Request object. Assign this value to a string variable.
19. Modify the GetPersonnel method you added to include a new parameter called strSearch of type string. This parameter needs to be after the Database string parameter that is already in the method.
20. When calling the GetPersonnel method, pass the value you received to the strSearch parameter.
21. In the GetPersonnel method, you now need to use the passed in strSearch parameter value as part of the SQL string being used to retrieve data. You also need to add logic so that, if strSearch is empty or has no value, all employees are returned in the query.
22. Test the search so that when you enter a last name, employees with that last name are returned. Make sure that when you access frmViewPersonnel and you are not searching, all employees are returned.
23. Lab Hints:
Make sure you re-establish your database connection if you copied the files from a previous lab.
Before you pass the search value into the GetPersonnel method, make sure you check to see if the Request item is null. If it is, you need to pass an empty string into the method or check for null inside the method. If you don't do this, you will get a server error. To check to see if an object is null, you compare the object to the keyword null.
To create an SQL statement that will search for a given last name in the tblPersonnel table, you can do the following (assume that the search variable was called strSearch).
"select * from tblPersonnel where LastName = '" + strSearch + "'"
24. Add the new Search option and the View Employees option to your main navigation page.STEP 3: Test and submit (10 points)
Learn More
Run your project and test it as follows:
The frmMain form should be displayed first (set this form as your start page).
Homepage
Click on the Add New Employee hyperlink to go to the frmPersonnel data entry form. Click the View Personnel button on this form. The frmViewPersonnel form should be displayed in the browser, but at this point, there should not be any personnel listed (because you haven't entered any yet).
Use the Back button in your web browser to return to the frmPersonnel form and enter some personnel data, similar to the following:
Entering Personnel Data
Now click the Submit button. The frmPersonnelVerified form should be displayed, showing the data you entered, and you should get a message saying that the data was successfully saved, like this:
Verifying Personnel Data
Finally, click the View Personnel data button on this form. The frmViewPersonnel form should be displayed and should show the personnel record you just entered, retrieved from the database, like this:
Viewing Personnel Data
You also should be able to view the employee records by clicking the link on the home page.
Test the search feature and make sure that entering no search string returns all the data and that typing in a last name will return all employees with the same last name.
Search
Search Results
NOTE: Make sure you include comments in the code provided where specified (where the " // Your comments here" line appears) and for any code you write, or else a five point deduction per item (form, class, function) will be made. -
CIS407 Lab 5 Week 5 Transaction Processing ASP.NET Web Application
$12.00This course has expired to download the latest version of CIS407A Labs click here
CIS 407 iLab 5 of 7: Transaction Processing
iLAB OVERVIEW
Scenario/Summary
This week, we will use the .NET OleDbTransaction functions to either commit a set of changes to the database, if all of them were done correctly, or to roll back all of the changes if there was an error in any one of them. We will first modify the code we created last week so that it saves personnel data in the database in two steps; first by inserting a personnel record for a new employee, and then by updating that record to fill in the start and end dates. This two-step approach is not really needed in this simple case, but we will use it to simulate a more complex database transaction that would have to be done in multiple steps, such as one involving more than one table or even more than one database. We will then see what happens when there is an error in the second operation (the update), allowing a record to be created containing incomplete information--not a good result! We will fix the problem by wrapping both operations (the insert and the update) into a single transaction that will be committed (made permanent) only if both operations succeed or that will be rolled back (undone) if either operation fails. We will also add client-side validation using the ASP.Net validation controls, and we will allow the user an easy way to edit all employees.
Instructions for Week 5 iLab: "Transaction Processing"Deliverables
All files are located in the subdirectory of the project. The project should function as specified: When you press the Submit button in frmPersonnel, a record should be saved in the tblPersonnel table containing the FirstName, LastName, PayRate, StartDate, and EndDate you entered. Test that the transaction will rollback by entering invalid information in one or more items, such as Hello for a StartDate. Check tht client-side validation works: The ability to edit employees in a grid is working. Once you have verified that it works, save your website, zip up all files, and submit them to the Dropbox.iLAB STEPS
STEP 1: Modify the clsDataLayer to use a two-step process (10 points)
1. Open Microsoft Visual Studio.NET 2008.
2. Click the ASP.NET project called PayrollSystem to open it.
3. Open the clsDataLayer class.
4. Modify the SavePersonnel() function so that instead of just doing a single SQL INSERT operation with all the personnel data, it does an INSERT with only the FirstName and LastName, followed by an UPDATE to save the PayRate, StartDate, and EndDate into the new record. (This two-step approach is not really necessary here because we are dealing with only one table, tblPersonnel, but we are doing it to simulate a case with more complex processing requirements, where we would need to insert or update data in more than one table or maybe even more than one database.) Find the following existing code in the SavePersonnel() function:
// Add your comments here
strSQL = "Insert into tblPersonnel " +
"(FirstName, LastName, PayRate, StartDate, EndDate) values ('" +
FirstName + "', '" + LastName + "', " + PayRate + ", '" + StartDate +
"', '" + EndDate + "')";
// Add your comments here
command.CommandType = CommandType.Text;
command.CommandText = strSQL;
// Add your comments here
command.ExecuteNonQuery();
5. Modify it so that it reads as follows:
// Add your comments here
strSQL = "Insert into tblPersonnel " +
"(FirstName, LastName) values ('" +
FirstName + "', '" + LastName + "')";
// Add your comments here
command.CommandType = CommandType.Text;
command.CommandText = strSQL;
// Add your comments here
command.ExecuteNonQuery();
// Add your comments here
strSQL = "Update tblPersonnel " +
"Set PayRate=" + PayRate + ", " +
"StartDate='" + StartDate + "', " +
"EndDate='" + EndDate + "' " +
"Where ID=(Select Max(ID) From tblPersonnel)";
// Add your comments here
command.CommandType = CommandType.Text;
command.CommandText = strSQL;
// Add your comments here
command.ExecuteNonQuery();
6. Set frmMain as the startup form and run the PayrollSystem Web application to test the changes. When valid data values are entered for a new employee, things should work exactly as they did before. To test this, enter valid data for a new employee in frmPersonnel and click Submit. The frmPersonnelVerified form should be displayed with the entered data values and a message that the record was saved successfully. Click the View Personnel button and check that the new personnel record was indeed saved to the database and that all the entered data values, including the PayRate, StartDate, and EndDate, were stored correctly. Close the browser window.
7. Now run the PayrollSystem Web application again, but this time enter some invalid data (a nonnumeric value) in the PayRate field to cause an error, like this:
frmPersonnel With Bad Data
8. Click here for text description of this image.
9. Now when you click Submit, the frmPersonnelVerified form should display a message indicating the record was not saved:
frmPersonnel Verified With Error Message
10. Click here for text description of this image.
11. However, when you click on the View Personnel button to display the personnel records, you should see that an incomplete personnel record was in fact created, with missing values for the PayRate, StartDate and EndDate fields:
Incomplete Personnel Record
12. Click here for text description of this image.
13. This occurred because the Insert statement succeeded but the following Update statement did not. We do not want to allow this to happen because we end up with incomplete or incorrect data in the database. If the Update statement fails, we want the Insert statement to be rolled back, or undone, so that we end up with no record at all. We will fix this by adding transaction code in the next step.STEP 2: Add transaction code (10 points)
7. In the clsDataLayer.cls class file, add code to the SavePersonnel() function to create a transaction object. Begin the transaction, commit the transaction if all database operations are successful, and roll back the transaction if any database operation fails. The following listing shows the complete SavePersonnel() function; the lines you will need to add are marked with ** NEW ** in the preceding comment and are shown in bold.
// This function saves the personnel data
public static bool SavePersonnel(string Database, string FirstName, string LastName,
string PayRate, string StartDate, string EndDate)
{
bool recordSaved;
// ** NEW ** Add your comments here
OleDbTransaction myTransaction = null;
try
{
// Add your comments here
OleDbConnection conn = new OleDbConnection("PROVIDER=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" +
"Data Source=" + Database);
conn.Open();
OleDbCommand command = conn.CreateCommand();
string strSQL;
// ** NEW ** Add your comments here
myTransaction = conn.BeginTransaction();
command.Transaction = myTransaction;
// Add your comments here
strSQL = "Insert into tblPersonnel " +
"(FirstName, LastName) values ('" +
FirstName + "', '" + LastName + "')";
// Add your comments here
command.CommandType = CommandType.Text;
command.CommandText = strSQL;
// Add your comments here
command.ExecuteNonQuery();
// Add your comments here
strSQL = "Update tblPersonnel " +
"Set PayRate=" + PayRate + ", " +
"StartDate='" + StartDate + "', " +
"EndDate='" + EndDate + "' " +
"Where ID=(Select Max(ID) From tblPersonnel)";
// Add your comments here
command.CommandType = CommandType.Text;
command.CommandText = strSQL;
// Add your comments here
command.ExecuteNonQuery();
// ** NEW ** Add your comments here
myTransaction.Commit();
// Add your comments here
conn.Close();
recordSaved = true;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// ** NEW ** Add your comments here
myTransaction.Rollback();
recordSaved = false;
}
return recordSaved;
}
8. Run your Web application. First, enter valid data in all the fields of frmPersonnel. When you press the Submit button in frmPersonnel, a record should be saved in the tblPersonnel table containing the FirstName, LastName, PayRate, StartDate, and EndDate. With valid data entered in all the items, the "successfully saved" message should appear indicating that the transaction was committed.
frmPersonnelVerified After Commit
9. Click here for text description of this image.
10. Click the View Personnel button and verify that the new record was in fact added to the database table correctly.
frmViewPersonnel After Commit
11. Click here for text description of this image.
12. Now close the browser, run the Web application again, and this time test that the transaction will roll back after entering incorrect information. On the frmPersonnel form, enter invalid data for PayRate and click Submit. The "not saved" message should appear, which indicates that the transaction was rolled back.
frmPersonnel Verified After Rollback
13. Click here for text description of this image.
14. Click the View Personnel button and verify that this time, as desired, an incomplete record was not added to the database table.
frmViewPersonnel After Rollback
15. Click here for text description of this image.
16. You have seen how we used the try/catch block to catch an unexpected error. You may have noticed that if you enter bad data for the dates, an exception is thrown. Go back to the validation code you added in the frmPersonnel code and add a try/catch with logic to prevent an invalid date from causing a server error.
17. In the Week 3 and Week 5 labs, you learned how to validate code once the page was posted back to the server. There is some validation that must be done on the server because it requires server resources such as the database. Some validation can also be done on the client. If you can do validation on the client it saves a round trip to the server, which will improve performance. In this approach, we will check values before the page is submitted to the server for processing. Normally, there is a combination of server and client validation used in a web application. ASP.Net includes validation controls which will use JavaScript on the client to perform validation. You will find these controls in the Validation group in the toolbox.
18. Add validation controls to the frmPersonnel form as follows: For the first and last name, make sure each field has data in it. Use the RequiredFieldValidator for this. Add the control to the right of the text box you are validating. The location of the validator control is where the error message (if there is one) will appear for the control you link the validator to. You will be adding one validator control for each text box you want to validate. Remember to set the ControlToValidate and ErrorMessage properties on the validator control. Making this change eliminates the need for the server-side check you were doing previously. Use a regular expression validator to check that the start and end date are in the correct format.
frmPersonnel Validation Controls
19. Click here for text description of this image.
20. Remove the View Personnel and Cancel buttons from the frmPersonnel form as they will cause a Postback and invoke the client-side editing you just added. The user is able to get to the View Personnel from the main form and from the personnel verification screen, so there is no need for these buttons now.
21. Because you have entered data in this lab that is invalid and those partial records are in the database, you will need to add the ability to remove or update data. Add a new main form option called Edit Employees. Add the link and image for this. This option will take the user to a new form called frmEditPersonnel.
frmMain with links added
22. Click here for text description of this image.
23. Add the new form frmEditPersonnel. On frmEditPersonnel, add the CoolBiz log at the top of the form. Add a label that says "Edit Employees." Add a GridView control with an ID of grdEditPersonnel.
24. You will now add a SQLDataSource to the page. You will be using a databound grid for this form unlike the previous grids, in which you added as unbound (in the designer).
25. Add a new SQLDataSource control to the frmEditPersonnel in the design view. This is not a visible control; that is, it will only appear in design view but the user will never see it. Note: If you change the folder name or location of your database, you will need to reconfigure the data source (right-click on the data source control and select the "Configure Data Source" option.
26. There is a small > indicator in the design view of the SQL Data Source control you added if the configuration menu is collapsed (press it to open the menu), or there is a < with the menu displayed. From the data source menu, select "Configure Data Source."
27. Press the New Connection button and select the database.
28. Press the Next button.
29. When asked if you want to save the connection in the application configuration file, check the Yes check box and press Next.
30. Select the tblPersonnel table.
31. Select all columns (you can use the * for this).
32. Press the Advanced button and check the Generate Insert, Update, and Delete option and press the OK button.
33. Press the Next button.
34. Press the Test Query button and make sure everything works as it is supposed to. If it does not repeat the above steps to make sure you did everything properly. Press the Finish button.
7. Click on the grid you added in the design view and expand the properties menu (the little > in the upper right of the control). Choose the data source you just added. On the GridView tasks menu, select Edit columns. Add an Edit, Update, and Cancel Command field. Add a Delete Command field. Press OK. You can now test the grid, which is a fully functioning Update and Delete grid. Try it out!
Edit Employees
8. Click here for text description of this image.
9. Hints: Make sure you re-establish your database connection if you copied the files from a previous lab.
In order to keep the validation controls from causing wrapping, you may want to increase the Panel width.
A regular expression for mm/dd/yyyy is this:
^(0[1-9]|1[012])[- /.](0[1-9]|[12][0-9]|3[01])[- /.](19|20)\d\d$
Experiment with the editable grid and command buttons for different display styles.STEP 3: Test and submit (10 points)
Learn More
29. Once you have verified that everything works as it is supposed to, save your project, zip up all files, and submit in the Dropbox.
NOTE: Make sure you include comments in the code provided where specified (where the " // Your comments here" is mentioned) and for any code you write, or else a five point deduction per item (form, class, function) will be made.





