Search results for 'Chapter 5: Apply Your Knowledge – Adding Fields, Using Input Mask and Querying Dates (Pages 327 - 328) Use the Babbage CPA'
Maximum words count is 10. In your search query was cut next part: Mask and Querying Dates (Pages 327 - 328) Use the Babbage CPA.
-
PRG/421 Week 3 Java 3.21 LAB: Plant information (ArrayList)
Regular Price: $6.00
Special Price $3.00
PRG/421 Week 3 Java 3.21 LAB: Plant information (ArrayList)
Given a base Plant class and a derived Flower class, complete main() to create an ArrayList called myGarden. The ArrayList should be able to store objects that belong to the Plant class or the Flower class. Create a method called printArrayList(), that uses the printInfo() methods defined in the respective classes and prints each element in myGarden. The program should read plants or flowers from input (ending with -1), adding each Plant or Flower to the myGarden ArrayList, and output each element in myGarden using the printInfo() method.
Ex. If the input is:
plant Spirea 10
flower Hydrangea 30 false lilac
flower Rose 6 false white
plant Mint 4
-1the output is:
Learn More
Plant Information:
Plant name: Spirea
Cost: 10
Plant Information:
Plant name: Hydrengea
Cost: 30
Annual: false
Color of flowers: lilac
Plant Information:
Plant name: Rose
Cost: 6
Annual: false
Color of flowers: white
Plant Information:
Plant name: Mint
Cost: 4 -
PRG/421 Week 3 Java 3.20 LAB: Book information (overriding member methods)
Regular Price: $6.00
Special Price $3.00
PRG/421 Week 3 Java 3.20 LAB: Book information (overriding member methods)
Given main() and a base Book class, define a derived class called Encyclopedia. Within the derived Encyclopedia class, define a printInfo() method that overrides the Book class' printInfo() method by printing not only the title, author, publisher, and publication date, but also the edition and number of volumes.
Ex. If the input is:
The Hobbit
J. R. R. Tolkien
George Allen & Unwin
21 September 1937
The Illustrated Encyclopedia of the Universe
James W. Guthrie
Watson-Guptill
2001
2nd
1the output is:
Book Information:
Book Title: The Hobbit
Author: J. R. R. Tolkien
Publisher: George Allen & Unwin
Publication Date: 21 September 1937
Book Information:
Book Title: The Illustrated Encyclopedia of the Universe
Author: James W. Guthrie
Publisher: Watson-Guptill
Publication Date: 2001
Edition: 2nd
Number of Volumes: 1Note: Indentations use 3 spaces.
Learn More -
PRG/421 Week 3 Java 3.19 LAB: Course information (derived classes)
Regular Price: $6.00
Special Price $3.00
PRG/421 Week 3 Lab 3.19 LAB: Course information (derived classes)
Given main(), define a Course base class with methods to set and get the courseNumber and courseTitle. Also define a derived class OfferedCourse with methods to set and get instructorName, term, and classTime.
Ex. If the input is:
ECE287
Digital Systems Design
ECE387
Embedded Systems Design
Mark Patterson
Fall 2018
WF: 2-3:30 pmthe output is:
Learn More
Course Information:
Course Number: ECE287
Course Title: Digital Systems Design
Course Information:
Course Number: ECE387
Course Title: Embedded Systems Design
Instructor Name: Mark Patterson
Term: Fall 2018
Class Time: WF: 2-3:30 pm -
PRG/421 Week 3 Java 3.18 LAB: Instrument information (derived classes)
Regular Price: $6.00
Special Price $3.00
PRG/421 Week 3 Lab 3.18 LAB: Instrument information (derived classes)
Given main() and the Instrument class, define a derived class, String Instrument, for string instruments.
Ex. If the input is:
Drums
Zildjian
2015
2500
Guitar
Gibson
2002
1200
6
19the output is:
Learn More
Instrument Information:
Name: Drums
Manufacturer: Zildjian
Year built: 2015
Cost: 2500
Instrument Information:
Name: Guitar
Manufacturer: Gibson
Year built: 2002
Cost: 1200
Number of strings: 6
Number of frets: 19 -
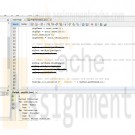
PRG/421 Week 3 Java 3.17 LAB: Pet information (derived classes)
Regular Price: $6.00
Special Price $3.00
PRG/421 Week 3 Lab 3.17 LAB: Pet information (derived classes)
The base class Pet has private fields petName, and petAge. The derived class Dog extends the Pet class and includes a private field for dogBreed. Complete main() to:
- create a generic pet and print information using printInfo().
- create a Dog pet, use printInfo() to print information, and add a statement to print the dog's breed using the getBreed() method.Ex. If the input is:
Dobby
2
Kreacher
3
German SchnauzerThe output is:
Learn More
Pet Information:
Name: Dobby
Age: 2
Pet Information:
Name: Kreacher
Age: 3
Breed: German Schnauzer -
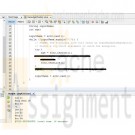
PRG/421 Week 3 Java 3.5 LAB: Exception handling to detect input String vs. Integer
Regular Price: $6.00
Special Price $3.00
PRG/421 Week 3 Java 3.5 LAB: Exception handling to detect input String vs. Integer
The given program reads a list of single-word first names and ages (ending with -1), and outputs that list with the age incremented. The program fails and throws an exception if the second input on a line is a String rather than an Integer. At FIXME in the code, add a try/catch statement to catch java.util.InputMismatchException, and output 0 for the age.
Ex: If the input is:
Lee 18
Lua 21
Mary Beth 19
Stu 33
-1then the output is:
Learn More
Lee 19
Lua 22
Mary 0
Stu 34 -
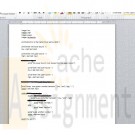
IT 140 Higher/Lower Game Pseudocode Project One
Regular Price: $8.00
Special Price $5.00
IT 140 Higher/Lower Game Pseudocode Project One
Higher/Lower Game Description
Your friend Maria has come to you and said that she has been playing the higher/lower game with her three-year-old daughter Bella. Maria tells Bella that she is thinking of a number between 1 and 10, and then Bella tries to guess the number. When Bella guesses a number, Maria tells her whether the number she is thinking of is higher or lower or if Bella guessed it. The game continues until Bella guesses the right number. As much as Maria likes playing the game with Bella, Bella is very excited to play the game all the time. Maria thought it would be great if you could create a program that allows Bella to play the game as much as she wants.For this assignment, you will be designing pseudocode for a higher/lower game program. The higher/lower game program uses similar constructs to the game you will design and develop in Projects one and Two.
1) Review the Higher/Lower Game Sample Output for more detailed examples of this game. As you read, consider the following questions:
What are the different steps needed in this program? How can you break them down in a way that a computer can understand?
What information would you need from the user at each point (inputs)? What information would you output to the user at each point?
When might it be a good idea to use "IF" and "IF ELSE" statements?
When might it be a good idea to use loops?2) Create a pseudocode that logically outlines each step of the game program so that it meets the following functionality:
Prompts the user to input the lower bound and upper bound. Include input validation to ensure that the lower bound is less than the upper bound.
Generates a random number between the lower and upper bounds
Prompts the user to input a guess between the lower and upper bounds. Include input validation to ensure that the user only enters values between the lower and upper bound.
Prints an output statement based on the guessed number. Be sure to account for each of the following situations through the use of decision branching:
What should the computer output if the user guesses a number that is too low?
What should the computer output if the user guesses a number that is too high?
What should the computer output if the user guesses the right number?
Loops so that the game continues prompting the user for a new number until the user guesses the correct number.OPTIONAL: If you would like to practice turning your designs into code, check out the optional 9.1 LAB: Higher/Lower Game in zyBooks. This step is optional but will give you additional practice turning designs into code, which will support your work in moving from Project One to Project Two.
Learn More -
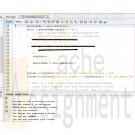
PRG/421 Week 4 Java 4.15 LAB: Ticketing service (Queue)
Regular Price: $7.00
Special Price $3.00
PRG/421 Week 4 Java 4.15 LAB: Ticketing service (Queue)
Given main, complete the program to add people to a queue. The program should read in a list of people's names including "You" (ending with -1), adding each person to the peopleInQueue queue. Then, remove each person from the queue until "You" is at the head of the queue. Include print statements as shown in the example below.
Ex. If the input is
Zadie Smith
Tom Sawyer
You
Louisa Alcott
-1the output is
Learn More
Welcome to the ticketing service...
You are number 3 in the queue.
Zadie Smith has purchased a ticket.
You are now number 2
Tom Sawyer has purchased a ticket.
You are now number 1
You can now purchase your ticket! -
PRG/421 Week 4 Java 4.14 LAB: Student grades (HashMap)
Regular Price: $7.00
Special Price $3.00
PRG/421 Week 4 Java 4.14 LAB: Student grades (HashMap)
Given a HashMap pre-filled with student names as keys and grades as values, complete main() by reading in the name of a student, outputting their original grade, and then reading in and outputting their new grade.
Ex: If the input is
Quincy Wraight
73.1the output is
Learn More
Quincy Wraight's original grade: 65.4
Quincy Wraight's new grade: 73.1 -
PRG/421 Week 4 Java 4.13 LAB: Grocery shopping list (LinkedList)
Regular Price: $7.00
Special Price $3.00
PRG/421 Week 4 Java 4.13 LAB: Grocery shopping list (LinkedList)
Given a ListItem class, complete the main() using the built-in LinkedList type to create a linked list called shoppingList. The program should read items from input (ending with -1), adding each item to shoppingList, and output each item in shoppingList using the printNodeData() method.
Ex. If the input is
milk
bread
eggs
waffles
cereal
-1the output is
Learn More
milk
bread
eggs
waffles
cereal





