Search results for 'cis 515'
-

COM 330 Chapter 6 Assignment
$20.00COM 330 Chapter 6 Assignment
Learn More
1. Using the STUDENT table structure shown in Table P6.4, do the following.
Table P6.4 Sample STUDENT Records
Attribute Name Sample Value Sample Value Sample Value Sample Value Sample Value
STU_NUM 211343 200128 199876 199876 223456
STU_LNAME Stephanos Smith Jones Ortiz McKulski
STU_MAJOR Accounting Accounting Marketing Marketing Statistics
DEPT_CODE ACCT ACCT MKTG MKTG MATH
DEPT_NAME Accounting Accounting Marketing Marketing Mathematics
DEPT_PHONE 4356 4356 4378 4378 3420
COLLEGE_NAME Business Admin Business Admin Business Admin Business Admin Arts & Sciences
ADVISOR_LNAME Grastrand Grastrand Gentry Tillery Chen
ADVISOR_OFFICE T201 T201 T228 T356 J331
ADVISOR_BLDG Torre Building Torre Building Torre Building Torre Building Jones Building
ADVISOR_PHONE 2115 2115 2123 2159 3209
STU_GPA 3.87 2.78 2.31 3.45 3.58
STU_HOURS 75 45 117 113 87
STU_CLASS Junior Sophomore Senior Senior Junior
c. Write the relational schema and draw the dependency diagram to meet the 3NF requirements to the greatest extent possible. If you believe that practical considerations dictate using a 2NF structure, explain why your decision to retain 2NF is appropriate. If necessary, add or modify attributes to create appropriate determinants and to adhere to the naming conventions.
d. Draw the Crow’s Foot ERD.
Load the data from table P6.4 into an Access database. Add 5 additional students (make up your data) following the table structure.
Create a query in Access that list the students who have a Statistics major.
List the students who have a GPA of 3.45 or higher in a report.
Report the students who have the same advisor.
Submit c and d as an attachment, attach your Access database. -
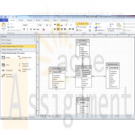
Coffee Merchant Enterprises (CM) and Home Warranty Corporation (HWC) Data Warehouse OLAP database
$20.00Coffee Merchant Enterprises (CM) and Home Warranty Corporation (HWC) Data Warehouse OLAP database
The purpose of this assignment is to promote students analytical skills in analyzing a case scenario and utilizing the given information and resources to design an ER diagram and develop an OLAP database.
1. Case Scenario
Coffee Merchant Enterprises (CM) sells coffee from a variety of different countries to consumers in the US. Their sales are all on-line. Their OLTP database for handling their day-to-day operations is shown in the ER Diagram below:CM wants to make data more available to their marketing analysts so that they can develop more effective marketing programs. They want to accomplish this goal without slowing down the performance of their existing OLTP system. They have decided to create a Data Warehouse to provide the information that the marketing analysts need. Your task is to design the database for the Data Warehouse.
The marketing analysts have asked for the ability to see sales data by product (inventory), consumer, employee who placed the order, and by various date variables including date, week, quarter, year, day of the week, and season. They do not need to see every sales but would need to see product sales summarized for each product on a daily basis.
2. Case Scenario
Consider the following ER Diagram for the OLTP database you designed from Home Warranty Corporation in the Case Project for Module 11. Your design may have differed from the one below, but this is the design that HWC decided to use.HWC has decided to develop a Data Warehouse so that they can analyze costs to assist in making a number of business decisions. For example, they want to determine if certain customers are costing more because they may be too hard on their appliances or if certain appliances that they cover tend to break down more than others, thus incurring more cost. Your task is to design the database for the Data Warehouse. The business managers have asked for the ability to see costs by customer, appliance, employee, and by various date variables including date, week, quarter, year, day of the week, and season. The need to see this cost information for every Service Call and need know the labor cost, material cost, and sum of both.
Learn More -
Succeeding in Business with Access Chapter 3 Case Problem 1 and 3
$25.00Succeeding in Business with Access 2010
Learn More
Chapter 3 Analyzing Data for Effective Decision Making
Case Problem Level 1 - managing Customer Information for NHD Development Group Inc.
Antiques.accdb complete solution from Step 1 - Step 12.
Case Problem Level 2 - Retrieving Employee Information for MovinOn Inc.
MovinOn.accdb complete solution from Step 1 - Step 12. -

CMIS 420 Final Project Advanced Relational Database Concepts and Applications
$20.00CMIS 420 Final Project Advanced Relational Database Concepts and Applications
Learn More
1. Description:
In the final project, you will demonstrate your ability to design, build, and populate a small data warehouse to support decision-making, business modeling, and operations research. Using data supplied by me, prepare a star schema and several queries that support decision-making. Submit the following deliverables:
1) SQL scripts showing the design, loading, and queries of the database.
2) results of running the script with the SQL*Plus spool command.
3) presentation to your fellow classmates describing the data warehouse, its design, and possible uses and applications for critical business decisions.
2. Tasks to be completed:
Based on our operational database, movie distributing and renting system (focus on movie distribution and sale), build a data mart (star schema) which can answer the following questions:
1) Which movie and\or movie category have the better sale by months and\or quarters?
2) Which distributor had best or better earnings (suppose profit margin is 12% for all the distributors) by months and\or quarters??
3) Which store should be the better sale target for movie sale?
The following link provides zip file containing a script to create a PL/SQL package which adds ordering records to your database. and another script to execute the procedures in the package to complete the tasks. At the end of execution, you will expect 500 to 1000 records in orders table and 3000 to 6000 records in order_items table. These data plus the existing data would serve you as operational data for your data warehousing project. The data in your dimension and fact tables should be derived from this database.
Run create_package.sql first, and then run_all.sql to execute the procedures in the package. -
CIS 373-30 SQL 1 EXERCISE
$20.00CIS 373-30 SQL 1 EXERCISE
Learn More
What to do:
Problem: ConstructionCo, pp. 278 – 282, Do problems 1 to 12 from page 278-280
You are given a partially correct Oracle script file: Ch07_ConstructCo_ORA.sql (posted in the same folder). The script is incomplete because they did not define primary keys and foreign keys when creating the tables. As shown in class (and also in my video capture), you will create your own script file based on this one by defining the primary keys and foreign keys (refer to the text book for the ERD).
To make it easier for you, I added several SQL Plus commands to redirect the output. At the beginning of the Ch07_ConstructCo_ORA.sql , I added:
spool j:\scripts\SQL1.lst
set pagesize 24
set pause on
set linesize 60
and at the very end, I added:
Spool out
The Spool command will redirect the output, in my case, to the J: drive in the scripts folder and the file will be called SQL1.lst (lst = listing, typical extension for output list). Make sure you know the path name to redirect the output to. I would recommend you to use the USB drive; make your path name shorter to avoid typos. Please also noted that I set the pause ON. It means that you have to hit “Enter” to move to the next page.
How to do:
(1) Start your Notepad, copy the necessary statements from Ch07_ConstructCo_ORA.sql with the proper PKs and FKs, save it as Ch07_SQL_1_Answers.sql.
(2) Log in Oracle 11g XE
(3) Start SQL Command Line (SQL Plus) program.
(4) In SQL Plus, load and execute Ch07_SQL_1_Answers.sql (by using the start command in SQL Plus.)
(5) To answer the questions, you can type your SQL statement directly in SQL Plus. If it works, copy and paste the statement in your script file Ch07_SQL_1_Answers.sql. Use comment, e.g. --, or /* …. */ to separate the questions. The following is the skeleton of your script file:
spool j:\scripts\SQL1.lst
set pagesize 24
set pause on
set linesize 60
-- Name: <Your Name> SQL 1 Homework, pp. 278-280
--
<<<< Based on Ch07_SQL_1_Answers.sql, create the tables with proper PKs and FKs. Copy all INSERT statements to populate the tables. Then you can start answering the questions. Make sure you have created and populated the tables correctly before moving forward. Do it incrementally like I demonstrated in the videos. >>>>
-- Problem 1:
select name from student where student_ID = 1234;
--
-- Problem 2:
insert into Student Values (13567, “Doe”, “John”, “CIS”);
: : : : :
-- Problem 12:
UPDATE EMP_2
SET …….
WHERE EMP_HIREDATE ….
AND JOB_CODE >= ….. ;
Spool out
After you have finished all problems and created the script file, run the script file in its entirety one last time. When you are finished, submit both Ch07_SQL_1_Answers.sql and the output file SQL1.lst in Blackboard. -
CIS355A iLab 1 ShowEscapeSequences Circle and PracticeArithmeticOperators Programs
$15.00CIS355A iLab 1 ShowEscapeSequences Circle and PracticeArithmeticOperators Programs
In this lab you will learn how to use the Java Software Development Kit (SDK) with the Eclipse programming tool. In addition, you will create three simple Java programs.
Deliverables
Program files for each of the following three programs.
1. ShowEscapeSequences.java
2. Circle.java
3. PracticeArithmeticOperators.java
At the beginning of ALL your programs, put a comment box that includes the program name, your name, and a brief description of the program.iLAB STEPS
STEP 1: ShowEscapeSequences (10 points)
Write a Java program named ShowEscapeSequences.java that displays the following.
I really like
CIS355A
"Business Application Programming with Lab using JAVA"STEP 2: Circle (15 points)
Write an application called Circle.java that inputs from the user the radius of a circle as an integer and prints the circle’s diameter, circumference, and area. Use the example program and GUI technique message dialog box shown in the Week 1 Lecture.
Use the following formulas.
diameter = 2 * radius
circumference = 2 * Math.PI * radius
area = Math.PI * radius * radius
Use the predefined constant Math.PI for your calculation. This constant is more precise than the value 3.14159. Class Math is defined in the java.lang package so you do not need to import it.STEP 3: PracticeArithmeticOperators (15 points)
Learn More
Write an application called PracticeArithmeticOperators.java that asks the user to enter two numbers. The program is to convert these numbers from String to type int and then print in a tabular format the sum, the difference, the product, and the quotient of the two numbers entered. Use the example program shown in the Week 1 Lecture. For example, if the user enters 25 and 5, the following should be displayed.
Operation Result
25 + 5 30
25 – 5 20
25 * 5 125
25 / 5 5 -
CIS355A iLab 2 Largest Palindrome and Diamond Programs
$15.00CIS355A iLab 2 Largest Palindrome and Diamond Programs
In this lab you will create programs that use control structures and user-defined methods.
Deliverables
Program files for each of the following three programs.
1. Largest
2. Palindrome
3. Diamond
At the beginning of ALL your programs, put a comment box that includes the program name, your name, and a brief description of the program.iLAB STEPS
STEP 1: Largest (10 points)
Write a Java application program called Largest.java that inputs a series of 10 single-digit numbers and determines and prints the largest of the numbers. Except main() method, no other user-defined method is required. Your program should use at least the following three variables
1. counter: A counter to count to 10 (that is, to keep track of how many numbers have been input and to determine when all 10 numbers have been processed);
2. number: The current digit input to the program; and
3. largest: The largest number found so far.
When each number is entered, make sure it is a single digit number, that is 0 to 9.STEP 2: Palindrome (15 points)
A palindrome is a sequence of characters that reads the same backward as forward. For example, each of the following five-digit integers is a palindrome: 12321, 55555, 45554, and 11611. Write an application called Palindrome.java that asks the user to enter in a five-digit integer and determines whether it is a palindrome. If the number is not five digits long, display an error message dialog indicating the problem to the user. When the user dismisses the error dialog, allow the user to enter a new value.
Your program will have the following four methods
1. main() method, which controls the execution of the program;
2. retrieveInput() method, which prompts and retrieves the input values;
3. check() method, which determines whether it is a palindrome; and
4. display() method, which displays the result.STEP 3: Diamond (15 points)
Learn More
Write a program called Diamond.java that uses a method diamondOfAsterisks() that displays a diamond (the row number of a diamond must be odd) of asterisks whose row is specified in an integer parameter row. For example, if the user enters a 7, then the diamond will have seven rows and the method will display the pattern of asterisks. Below is an example of the diamond displayed when 7 is entered.
*
***
*****
*******
*****
***
* -
CIS355A iLab 3 Cylinder and Date Java Programs
$15.00CIS355A iLab 3 Cylinder and Date Java Programs
In This lab you will create two programs that use classes and methods.
Deliverables
Program files for each of the following two programs
1. Cylinder
2. DateiLAB STEPS
STEP 1: Cylinder
Create a class called Cylinder.java that contains two double-precision instance variables named radius and height. The class should include a constructor that initializes the radius and height variables. Also, you need a class method named volume() that returns the volume of a Cylinder object. The volume of a cylinder is given by its radius squared times its height times Pi (radius * radius * height * Math.PI). You can either use the value 3.1416 for Pi or use the Java provided value named Math.PI.
Write a class called CylinderTest.java and declare an array of three Cylinder objects to call the methods you declared in the Cylinder class. Make sure that all class methods are called from main(). Have main() display the value returned by volume() and verify the returned value by hand calculations (paper/pencil). Prompt the user to enter the values for the radius and height of each Cylinder object in the array.
Learn More
STEP 2: Date (20 points)
Create a program called Date.java to perform error-checking on the initial values, for instance: fields month, day, and year. Also, provide a method nextDay() to increment the day by one. The Date object should always remain in a consistent state.
Write a program called DateTest.java that prompts the user to enter the month, day, and year as numeric values. This program then creates a Date object using the Date class you just created and tests the nextDay() method. This can be done in a loop of 40 iterations: the Date object calls the nextDay() method and prints the date during each iteration of the loop. This loop is to illustrate that the nextDay() method works correctly. Test the following cases:
a. Incrementing into the next month, for example, use date: 02/28/2011
b. Incrementing into the next year, for example, use date: 11/27/2011
c. Incrementing into the next month in a leap year, for example, use date: 02/28/2012
Sample Program Output:
Checking increment
Date object constructor for date 11/27/2011
Incremented Date:11/28/2011
Incremented Date:11/29/2011
Incremented Date:11/30/2011
Day 31 invalid. Set to day 1.
Incremented Date:12/1/2011
Incremented Date:12/2/2011
...
Incremented Date:12/30/2011
Incremented Date:12/31/2011
Day 32 invalid. Set to day 1.
Incremented Date:1/1/2012
Incremented Date:1/2/2012
Incremented Date:1/3/2012
Incremented Date:1/4/2012
Incremented Date:1/5/2012
Incremented Date:1/6/2012 -
CIS355A iLab 4 InheritanceTest DayGui and OfficeAreaCalculator Java Programs
$15.00CIS355A iLab 4 InheritanceTest DayGui and OfficeAreaCalculator Java Programs
In this lab, you will create one project that uses inheritance and two simple Graphical User Interfaces (GUI) programs.
Deliverables
Program files for each of the following three programs
1. InheritanceTest
2. DayGui
3. OfficeAreaCalculatoriLAB STEPS
STEP 1: InheritanceTest (20 points)
Write a program called InheritanceTest.java to support an inheritance hierarchy for class Point-Square-Cube. Use Point as the superclass of the hierarchy. Specify the instance variables and methods for each class. The private variable of Point should be the x-y coordinates. The private data of Square should be the sideLength. The private data of Cube should be depth. Each class must provide applicable accessor, mutator, and toString() methods for manipulating private variables of each corresponding class. In addition, the Square class must provide the area() and perimeter() methods. The Cube must provide the area() and volume() methods.
Write a program that instantiates objects of your classes, ask the user to enter the value for x, y, and sideLength, test all instance methods and outputs of each object’s perimeter, area, and volume when appropriate.STEP 2: DayGui (10 points)
Write a program called DayGui.java that creates a GUI having the following properties
Object Property Setting
JFrame Name Caption Layout mainFrame Messages FlowLayout
JButton Name Caption Mnemonic cmdGood Good G
JButton Name Caption Mnemonic cmdBad Bad B
Add individual event handlers to your program so that when a user clicks the Good button, the message "Today is a good day!" appears in a dialog box, and when the Bad button is clicked, the message "I'm having a bad day today!" is displayed. The following tutorial shows you much of the code solution. Feel free to use the tutorial, but make changes so that you are not simply copying the tutorial code for your entire solution. To make this different from the tutorial, change the colors of the buttons and panel. Also, add this application to a tabbed pane along with the program you will complete in the next step, Step 3. The following tutorials will likely be useful as you work to complete this step:
• JTabbedPane
• Tutorial to Write Your First GUISTEP 3: OfficeAreaCalculator (10 points)
Learn More
Write a program called OfficeAreaCalculator.java that displays the following prompts using two label components
• Enter the length of the office:
• Enter the width of the office:
Have your program accept the user input in two text fields. When a button is clicked, your program should calculate the area of the office and display the area in a text field with a label of Area. This display should be cleared whenever the input text fields receive the focus. A second button should be provided to terminate the application (Exit button).
The following tutorial shows you much of the code solution. Feel free to use the tutorial, but make changes so that you are not simply copying the tutorial code for your entire solution. To make this different from the tutorial, change the colors of the panel. Also, add this application to the same tabbed pane (see the JTabbedPane tutorial) as the application you built in Step 2, the DayGui application.
• Office Area Calculator Tutorial -
CIS355A iLab 5 GuessGame and Text File I/O Java Programs
$15.00CIS355A iLab 5 GuessGame and Text File I/O Java Programs
In this lab you will create a single program that creates and reads a sequential file. All outputs must be GUI-based without using JOptionPane.
Deliverables
Program files for each of the following two programs
1. GuessGame
2. Text File I/OiLAB STEPS
STEP 1: GuessGame
Write a program named GuessGame.java that plays the game “guess the number” as follows: Your program chooses the number to be guessed by selecting an integer at random in the range 1–1000. The program then displays the following in a label.
I have a number between 1 and 1000 -- can you guess my number?
Please enter your guess: ____________________
A JTextField should be used to input the guess. A JButton must be provided to allow the user to press each time a guess is entered. As each guess is input, the background color should change to either red or blue. Red indicates that the user is getting warmer, and blue indicates that the user is getting colder. A JLabel should display either Too High or Too Low to help the user zero in on the correct answer. When the user gets the correct answer, Correct! should be displayed, and the JTextField used for input should be cleared and changed to be uneditable. Also, a JButton should be provided to allow the user to play the game again. When the New Game JButton is clicked, a new random number should be generated and the input JTextField changed to be editable. A JButton must be provided to allow the user to exit the application. Also provide a count of the number of guesses the user entered when the correct number is guessed.STEP 2: Text File I/O (20 points)
Learn More
Write a program called TextFileIO.java to create a file named numbers.dat. Then create an algorithm that writes all even numbered integers from 1 to 100, separated by a comma. After the file has been created, close and reopen the file and display the results to the screen. After the results have been displayed append the odd number integers from 1 to 100, separated by a comma to the end of the file. Reopen the file and display the results. The contents of the file should be the even numbers from 1 to 100 separated by a comma followed by the odd number from 1 to 100 separated by a comma. The output of this program would be something like the following
2,4,6,8,10,12,14,……,98,100
2,4,6,8,10,12,14,……,98,100,1,3,5,7,9,……..97,99





