Search results for 'capstone wee ones daycare'
-
DAT/305 Week 3 Challenge Activities 3.6.1: Hash tables with modulo hash function
Regular Price: $5.00
Special Price $3.00
DAT/305 Week 3 Challenge Activities 3.6.1: Hash tables with modulo hash function
CHALLENGE ACTIVITY 1
A hash table with non-negative integer keys has a modulo hash function of key % 20.
Hash function index range: 0 to
Item 128 will go in bucket
CHALLENGE ACTIVITY 2An ordinary array contains items with keys: 30, 22, 6, 34, 2, 10,13
A hash table has 15 buckets with hash function key % 15.
The hash table contains the same items as the array.How many elements are checked when searching for each of the following items?
CHALLENGE ACTIVITY 3An empty hash table hashTable has 5 buckets and a hash function of key % 5.
Learn More
The following operations are performed in order.
Select which operations cause a collision.
Hashinsert(hash Table, 2)
Hashinsert(hashTable, 12)
Hashinsert(hashTable, 0)
Hashinsert(hashTable, 5)
Hashinsert(hash Table, 15) -
DAT/305 Week 3 Challenge Activities 3.5.1: Deque ADT
Regular Price: $5.00
Special Price $3.00
DAT/305 Week 3 Challenge Activities 3.5.1: Deque ADT
CHALLENGE ACTIVITY 1
Given an empty deque numDeque, what are the deque's contents after the following operations?
PushBack(numDeque, 24)
PushFront(numDeque, 49)
PushBack(numDeque, 44)After the above operations, what does PeekFront(numDeque) return?
After the above operations, what does PeekBack(numDeque) return?
After the above operations, what does GetLength(numDeque) return?
CHALLENGE ACTIVITY 2Given an empty deque numDeque, what are the deque's contents after the following operations?
PushBack(numDeque, 95)
PopFront(numDeque)
PushFront(numDeque, 42)
PushFront(numDeque, 25)
PopBack(numDeque)After the above operations, what does GetLength(numDeque) return?
CHALLENGE ACTIVITY 3Given numDeque: 19, 38
PeekFront(numDeque)
PopFront(numDeque)
After the above operations, what does GetLength(numDeque) return?After the above operations, what does IsEmpty(numDeque) return?
Learn More -
DAT/305 Week 3 Challenge Activities 3.4.1: Queues using linked lists
Regular Price: $5.00
Special Price $2.00
DAT/305 Week 3 Challenge Activities 3.4.1: Queues using linked lists
CHALLENGE ACTIVITY 1
Given an empty queue numQueue, what does the list head pointer point to? If the pointer is null, enter null.
What does the list tail pointer point to?
After the following operations:
QueueEnqueue(numqueue, 66)
QueueEnqueue(numQueue, 93)
QueueDequeue(numQueue)What does the list head pointer point to?
What does the list tail pointer point to?
CHALLENGE ACTIVITY 2Given numQueue: 78, 37, 47
What does the list head pointer point to? If the pointer is null enter null.
What does the list tail pointer point to?
After the following operations:
QueueEnqueue(numQueue, 60)
QueueEnqueue(numqueue, 57)
QueueDequeue(numQueue)
QueueDequeue(numQueue)What does the list head pointer point to?
What does the list tail pointer point to?
Learn More -
DAT/305 Week 3 Challenge Activities 3.3.1: Queue ADT
Regular Price: $5.00
Special Price $4.00
DAT/305 Week 3 Challenge Activities 3.3.1: Queue ADT
CHALLENGE ACTIVITY 1
Given numQueue: 75, 45
What are the queue's contents after the following operations?
Enqueue (numQueue, 80)
Dequeue(numQueue)After the above operations, what does GetLength(numQueue) return?
CHALLENGE ACTIVITY 2Given numQueue: 90, 60
What does Peek(numQueue) return?What is the queue after the following operations?
Peek(numQueue)
Dequeue (numQueue)
Peek(numQueue)
Enqueue (numQueue, 90)After the above operations, what does GetLength(numqueue) return?
CHALLENGE ACTIVITY 3Given numQueue: 73, 39
Peek(numQueue)
Dequeue (numqueue)
After the above operations, what does GetLength(numQueue) return?After the above operations, what does IsEmpty(numQueue) return?
CHALLENGE ACTIVITY 4Given numQueue is empty, what does the list head pointer point to?
What does the list tail pointer point to?
After the following operations:
Enqueue (numQueue, 26)
Enqueue (numQueue, 47)
Enqueue (numQueue, 22)
Dequeue (numQueue)What does the list head pointer point to?
What does the list tail pointer point to?
Learn More -
DAT/305 Week 3 Challenge Activities 3.2.1: Stacks using linked lists
Regular Price: $5.00
Special Price $3.00
DAT/305 Week 3 Challenge Activities 3.2.1: Stacks using linked lists
CHALLENGE ACTIVITY 1
Given an empty stack numStack, what does the list head pointer point to? If the pointer is null, enter null.
After the following operation, which node does the list head pointer point to?
StackPush(numStack, 83)
CHALLENGE ACTIVITY 2Given numStack: 54, 38, 25, 28 (top is 54)
After the following operation: StackPush(numStack, 40)
What node does newNode's next pointer point to? If the pointer is null, enter null.What node does the list's head pointer point to?
CHALLENGE ACTIVITY 3Given numStack: 51 (top is 51)
After the following operation: StackPop(numStack)
What is returned?What node does the list's head pointer point to? If the pointer is null, enter null:
Learn More -
DAT/305 Week 3 Challenge Activities 3.1.1: Stack ADT
Regular Price: $5.00
Special Price $3.00
DAT/305 Week 3 Challenge Activities 3.1.1: Stack ADT
CHALLENGE ACTIVITY 1
Given numStack: 69,87 (top is 69)
What is the stack after the following operations?
Pop(numStack)
Push(numStack, 92)
Pop(numStack)
Push(numStack, 77)After the above operations, what does GetLength(numStack) return?
CHALLENGE ACTIVITY 2
Given numStack: 11,71,12 top is 11)
What does Peek(numStack) return?What is the stack after the following operations?
Push(numStack, 34)
Pop(numStack)
Push(numStack, 73)
Peek numStack)
Peek/numStack)After the above operations, what does GetLength(numStack) return?
CHALLENGE ACTIVITY 3Given numStack: 16.65 (top is 16)
Pop(numStack)
Pop(numStack)After the above operations, what does GetLength(numStack) return?
After the above operations, what does isEmpty(numStack) return?
Learn More -
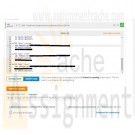
DAT/380 Week 5 LAB 5.7 - Implement supertype and subtype entities (Sakila)
Regular Price: $5.00
Special Price $3.00
DAT/380 Week 5 LAB 5.7 - Implement supertype and subtype entities (Sakila)
Refer to the customer and staff tables of the Sakila database. These tables have many columns in common and represent similar entities. Convert the customer and staff entities into subtypes of a new supertype person:
In the center is the person entity, with primary key person_id and additional attributes first_name, last_name, email, active, and last_update. The person entity contains subtype entities staff and customer. The staff entity has primary key person_id and additional attributes picture, username, and password. The customer entity has primary key person_id and additional attribute create_date. Cardinality does not appear after the primary keys and attributes. On the left is the address entity, connected to the person entity by the belongs_to relationship. Belongs_to has cardinality 1(1) on the address side and M(0) on the person side. On the right is the store entity, connected to the person entity by the works_at relationship. Works_at has cardinality 1(1) on the store side and M(0) on the person side.
The diagram uses Sakila naming conventions. Follow the Sakila conventions for your table and column names:
All lower case
Underscore separator between root and suffix
Foreign keys have the same name as referenced primary keyImplement supertype and subtype entities as person, customer, and staff tables with primary key person_id.
Implement attributes as columns:
All columns are NOT NULL.
The person_id columns have data type SMALLINT UNSIGNED.
The last_update and create_date columns have data type TIMESTAMP.
The picture column has data type BLOB.
All other columns have data type VARCHAR(20).Implement the dependency relationships between subtype and supertype entities as foreign keys:
The person_id columns of customer and staff become foreign keys referring to person.
Specify CASCADE actions for both relationships.Implement the belongs_to and works_at relationships as foreign keys:
belongs_to becomes an address_id foreign key in person referring to address.
works_at becomes a store_id foreign key in staff referring to store.
Specify RESTRICT actions for both relationships.The address and store tables, with primary keys address_id and store_id, are pre-defined in the zyLab environment. Foreign keys must have the same data types as the referenced primary keys:
address_id has data type SMALLINT UNSIGNED.
store_id has data type TINYINT UNSIGNED.If you execute your solution with the Sakila database, you must first drop customer, staff, and all constraints that refer to these tables. Use the following statements with Sakila only, not in the zyLab environment:
Learn More
DROP TABLE customer, staff;
ALTER TABLE payment
DROP CONSTRAINT fk_payment_customer,
DROP CONSTRAINT fk_payment_staff;
ALTER TABLE rental
DROP CONSTRAINT fk_rental_customer,
DROP CONSTRAINT fk_rental_staff;
ALTER TABLE store
DROP CONSTRAINT fk_store_staff; -
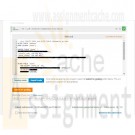
DAT/380 Week 5 LAB 5.6 - Implement independent entity (Sakila)
Regular Price: $5.00
Special Price $3.00
DAT/380 Week 5 LAB 5.6 - Implement independent entity (Sakila)
Implement a new independent entity phone in the Sakila database. Attributes and relationships are shown in the following diagram:
The phone entity appears on the right. The phone entity contains four attributes, each followed by cardinality information: phone_id 1-1(1), country_code M-1(1), phone_numer M-1(1), and phone_type M-1(0). Three entities appear on the left: store, staff, and customer, connected to the phone entity by three identical relationships. The three relationships are named 'has' and have cardinality 1(0) on both sides.
The diagram uses Sakila naming conventions. Follow the Sakila conventions for your table and column names:
All lower case
Underscore separator between root and suffix
Foreign keys have the same name as referenced primary keyWrite CREATE TABLE and ALTER TABLE statements that:
1. Implement the entity as a new phone table.
2. Implement the has relationships as foreign keys in the Sakila customer, staff, and store tables.
3. Remove the existing phone column from the Sakila address table.Step 2 requires adding a foreign key constraint to an existing table. Ex:
ALTER TABLE customer
ADD FOREIGN KEY (phone_id) REFERENCES phone(phone_id)
ON DELETE SET NULL
ON UPDATE CASCADE;
Specify data types as follows:
phone_id, phone_number, and country_code have data type INT.
phone_type has date type VARCHAR(12) and contains strings like 'Home', 'Mobile', and 'Other'.Apply these constraints:
Learn More
NOT NULL constraints correspond to cardinalities on the diagram above.
Foreign key actions are SET NULL for delete rules and CASCADE for update rules.
Specify a suitable column as the phone table primary key. -
DAT/380 Week 4 LAB 4.7 - Select number of movies grouped by year
Regular Price: $5.00
Special Price $3.00
DAT/380 Week 4 LAB 4.7 - Select number of movies grouped by year
The Movie table has the following columns:
ID - integer, primary key
Title - variable-length string
Genre - variable-length string
RatingCode - variable-length string
Year - integerWrite a SELECT statement to select the year and the total number of movies for that year.
Hint: Use the COUNT() function and GROUP BY clause
Learn More -
DAT/380 Week 4 LAB 4.6 - Select lesson schedule with inner join
Regular Price: $5.00
Special Price $3.00
DAT/380 Week 4 LAB 4.6 - Select lesson schedule with inner join
The database has three tables for tracking horse-riding lessons:
Horse with columns:
ID - primary key
RegisteredName
Breed
Height
BirthDateStudent with columns:
ID - primary key
FirstName
LastName
Street
City
State
Zip
Phone
EmailAddressLessonSchedule with columns:
HorseID - partial primary key, foreign key references Horse(ID)
StudentID - foreign key references Student(ID)
LessonDateTime - partial primary keyWrite a SELECT statement to create a lesson schedule with the lesson date/time, horse ID, and the student's first and last names. Order the results in ascending order by lesson date/time, then by horse ID. Unassigned lesson times (student ID is NULL) should not appear in the schedule.
Hint: Perform a join on the Student and LessonSchedule tables, matching the student IDs.
Learn More




