Search results for 'Patton-Fuller Database Design Process Project DBM/502'
-
CIS115 Week 1 Lab Building a Registration Form and Pay Calculator in Python
Regular Price: $12.00
Special Price $10.00
CIS115 Week 1 Lab Building a Registration Form and Pay Calculator in Python
CIS115 Week 1 Lab Overview
Title of Lab: Building a Registration Form and Pay Calculator in Python
Summary – Part 1
Create a program that allows a student to complete a registration form and displays a completion message that includes the user's full name and a temporary password.Summary – Part 2
Create a program that calculates a user's weekly gross and take-home pay.Deliverables
• 2 source code Python files.
• A Word document containing both source code and the screen print of the program outputs.Lab Steps
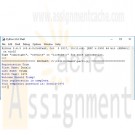
Part 1 – Registration FormSample Output:
Registration Form
First Name: Eric
Last Name: Idle
Birth Year: 1934
Welcome Eric Idle!
Your Registration is complete.
Your temporary password is: Eric*1934Specifications:
• The user's full name consists of the user's first name, a space, and the user's last name.
• The temporary password consists of the user's first name, an asterisk (*), and the user's birth year.
• Assume the user will enter valid data.INPUT PROCESSING OUTPUT
first_name password=first_name + "*" + str(birth_year) password
last_name
birth_year
Part 2 – Pay CalculatorSample Output:
Pay Check Calculator
Hours Worked: 35
Hourly Pay Rate: 14.50
Gross Pay: 507.5
Tax Rate: 18
Tax Amount: 91.35
Take Home Pay: 416.15• The formula for calculating gross pay is:
o gross pay = hours worked * hourly rate
• The formula for calculating tax amount is:
o tax amount = gross pay * (tax rate / 100)
• The formula for calculating take home pay is:
o take home pay = gross pay - tax amount
• The tax rate should be 18%, but the program should store the tax rate in a variable so that you can easily change the tax rate later, just by changing the value that's stored in the variable.
• The program should accept decimal entries like 35.5 and 14.25.
• Assume the user will enter valid data.
• The program should round the results to a maximum of two decimal places.INPUT PROCESSING OUTPUT
Learn More
hours gross_pay = round(hours * pay_rate, 2) gross_pay
pay_rate tax_rate = 18 tax_rate
tax_amount = round(gross_pay * (tax_rate / 100), 2) tax_amount
take_home_pay = round(gross_pay - tax_amount, 2) take_home_pay -
CYB/130 Week 2 Python LAB 3.13: Input and formatted output: House real estate summary
Regular Price: $8.00
Special Price $3.00
CYB/130 Week 2 Python LAB 3.13: Input and formatted output: House real estate summary
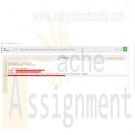
Sites like Zillow get input about house prices from a database and provide nice summaries for readers. Write a program with two inputs, current price and last month's price (both integers). Then, output a summary listing the price, the change since last month, and the estimated monthly mortgage computed as (current_price * 0.051) / 12.Output each floating-point value with two digits after the decimal point, which can be achieved as follows:
print('{:.2f}'.format(your_value))Ex: If the input is:
200000
210000
the output is:
This house is $200000. The change is $-10000 since last month.
The estimated monthly mortgage is $850.00.Note: Getting the precise spacing, punctuation, and newlines exactly right is a key point of this assignment. Such precision is an important part of programming.
Learn More -

PRG/211 Week 1 Lab 3.3: House real estate summary
Regular Price: $8.00
Special Price $3.00
PRG/211 Week 1 Lab 3.3.1: House real estate summary
Sites like Zillow get input about house prices from a database and provide nice summaries for readers. Write a program with two inputs, current price and last month's price (both integers). Then, output a summary listing the price, the change since last month, and the estimated monthly mortgage computed as (currentPrice * 0.045) / 12.
Ex: If the input is 200000 210000, the output is:
This house is $200000. The change is $-10000 since last month.
Learn More
The estimated monthly mortgage is $750.0.
Note: Getting the precise spacing, punctuation, and newlines exactly right is a key point of this assignment. Such precision is an important part of programming. -
CIS115 Course Project Guess The Number
Regular Price: $15.00
Special Price $12.00
CIS115 Course Project Guess The Number
You will create a program that will ask the user to guess a number between 1 and 10. The pseudocode is below. Be sure to import random at the beginning of your code and use a comment block explaining what your program does
#Guess the number week 4
#Name:
#Date:
#Random number, loop while true
#ask user for number.
#if number is too high or too low, tell user, if they guessed it break out of loopDisplay "Welcome to my Guess the number program!"
random mynumber
while True
Display "Guess a number between 1 and 10"
Get guess
if (guess<mynumber)
Display "Too low"
else if (guess>mynumber)
Display "Too high"
else if (guess==mynumber)
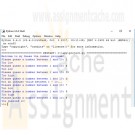
Display "You guessed it!"When you run your program the result should be something like this:
Welcome to my Guess the number program!Please guess a number between 1 and 10: 5
Too high
Please guess a number between 1 and 10: 4
Too high
Please guess a number between 1 and 10: 3
Too high
Please guess a number between 1 and 10: 2
You guessed it!Be sure to submit your assignment
Learn More -
DAT/210 Week 5 Python LAB 6.22: Python and sqlite basics
Regular Price: $10.00
Special Price $4.00
DAT/210 Week 5 Python LAB 6.22: Python and sqlite basics
Write a Python program that connects to a sqlite database.
Create a table called Horses with the following fields:
• id (integer): a primary key and not null
• name (text)
• breed (text)
• height (real)
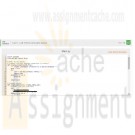
• birthday (text)Next, insert the following data row into the Horses table:
Learn More
id: 1
name: 'Babe'
breed: 'Quarter Horse'
height: 15.3
birthday: '2015-02-10'
Output all records from the Horses table.
Ex: With the above row inserted, the output should be:
All Horses:
(1, 'Babe', 'Quarter Horse', 15.3, '2015-02-10') -
DAT/210 Week 5 Python 6.23: Python insert/update sqlite3 datafiles
Regular Price: $10.00
Special Price $4.00
DAT/210 Week 5 Python 6.23: Python insert/update sqlite3 datafiles
Given is a Python program that connects to a sqlite database and has one table called writers with two columns:
• name - the name of a writer
• num - the number of works the writer has writtenThe writers table originally has the following data
name, num
Jane Austen,6
Charles Dickens,20
Ernest Hemingway,9
Jack Kerouac,22
F. Scott Fitzgerald,8
Mary Shelley,7
Charlotte Bronte,5
Mark Twain,11
Agatha Christie,73
Ian Flemming,14
J.K. Rowling,14
Stephen King,54
Oscar Wilde,1
Update the Python program to ask the user if they want to update entries or add new entries. If the name entered already exists in the writers table then the database record is updated, overwriting the original contents. If the name does not exist in the writers table, then add a new record with the writers name and number of works. The following TODO sections must be completed.
• Check if a writer exists in the writers table
• If the writer exists in the table, locate an entry to be updated by writers name and update the writer's value for num
• If the writer does not exist in the table, add a new entry in the writers table and provide the value for name and numEx if the input is:
Learn More
y
J.K. Rowling
30
y
Elton John
y
62
n
The output is:
(ID, Name, Num)
(1, 'Jane Austen', 6)
(2, 'Charles Dickens', 20)
(3, 'Ernest Hemingway', 9)
(4, 'Jack Kerouac', 22)
(5, 'F. Scott Fitzgerald', 8)
(6, 'Mary Shelley', 7)
(7, 'Charlotte Bronte', 5)
(8, 'Mark Twain', 11)
(9, 'Agatha Christie', 73)
(10, 'Ian Flemming', 14)
(11, 'J.K. Rowling', 30)
(12, 'Stephen King', 54)
(13, 'Oscar Wilde', 1)
(14, 'Elton John', 62) -
IT 140 Higher/Lower Game Pseudocode Project One
Regular Price: $8.00
Special Price $5.00
IT 140 Higher/Lower Game Pseudocode Project One
Higher/Lower Game Description
Your friend Maria has come to you and said that she has been playing the higher/lower game with her three-year-old daughter Bella. Maria tells Bella that she is thinking of a number between 1 and 10, and then Bella tries to guess the number. When Bella guesses a number, Maria tells her whether the number she is thinking of is higher or lower or if Bella guessed it. The game continues until Bella guesses the right number. As much as Maria likes playing the game with Bella, Bella is very excited to play the game all the time. Maria thought it would be great if you could create a program that allows Bella to play the game as much as she wants.For this assignment, you will be designing pseudocode for a higher/lower game program. The higher/lower game program uses similar constructs to the game you will design and develop in Projects one and Two.
1) Review the Higher/Lower Game Sample Output for more detailed examples of this game. As you read, consider the following questions:
What are the different steps needed in this program? How can you break them down in a way that a computer can understand?
What information would you need from the user at each point (inputs)? What information would you output to the user at each point?
When might it be a good idea to use "IF" and "IF ELSE" statements?
When might it be a good idea to use loops?2) Create a pseudocode that logically outlines each step of the game program so that it meets the following functionality:
Prompts the user to input the lower bound and upper bound. Include input validation to ensure that the lower bound is less than the upper bound.
Generates a random number between the lower and upper bounds
Prompts the user to input a guess between the lower and upper bounds. Include input validation to ensure that the user only enters values between the lower and upper bound.
Prints an output statement based on the guessed number. Be sure to account for each of the following situations through the use of decision branching:
What should the computer output if the user guesses a number that is too low?
What should the computer output if the user guesses a number that is too high?
What should the computer output if the user guesses the right number?
Loops so that the game continues prompting the user for a new number until the user guesses the correct number.OPTIONAL: If you would like to practice turning your designs into code, check out the optional 9.1 LAB: Higher/Lower Game in zyBooks. This step is optional but will give you additional practice turning designs into code, which will support your work in moving from Project One to Project Two.
Learn More -

PRG 211 Week 1 Labs
Regular Price: $15.00
Special Price $12.00
Lab 3.1 Formatted Output Hello World!
Write a program the outputs 'Hello World!'
Lab 3.2 Formatted output: No parking sign.Write a program that prints a formatted "No parking" sign. Note the first line has two leading spaces.
NO PARKING
1:00 - 5:00 a.m.
Lab 3.3 House real estate summarySites like Zillow get input about house prices from a database and provide nice summaries for readers. Write a program with two inputs, current price and last month's price (both integers). Then, output a summary listing the price, the change since last month, and the estimated monthly mortgage computed as (currentPrice * 0.045) / 12.
Ex: If the input is 200000 210000, the output is:
This house is $200000. The change is $-10000 since last month.
The estimated monthly mortgage is $750.0.
Note: Getting the precise spacing, punctuation, and newlines exactly right is a key point of this assignment. Such precision is an important part of programming.
Lab 3.4 Caffeine levelsA half-life is the amount of time it takes for a substance or entity to fall to half its original value. Caffeine has a half-life of about 6 hours in humans. Given caffeine amount (in mg) as input, output the caffeine level after 6, 12, and 18 hours.
Ex: If the input is 100, the output is:
After 6 hours: 50.0 mg
After 12 hours: 25.0 mg
After 18 hours: 12.5 mg
Note: A cup of coffee has about 100 mg. A soda has about 40 mg. An "energy" drink (a misnomer) has between 100 mg and 200 mg.
Lab 3.5 Divide by x.Write a program using integers userNum and x as input, and output userNum divided by x four times.
Ex: If the input is 2000 2, the output is:
1000 500 250 125
Note: In Coral, integer division discards fractions. Ex: 6 / 4 is 1 (the 0.5 is discarded).
Lab 3.6 Driving costs.Driving is expensive. Write a program with a car's miles/gallon and gas dollars/gallon (both floats) as input, and output the gas cost for 10 miles, 50 miles, and 400 miles.
Ex: If the input is 20.0 3.1599, the output is:
1.57995 7.89975 63.198
Note: Small expression differences can yield small floating-point output differences due to computer rounding. Ex: (a + b)/3.0 is the same as a/3.0 + b/3.0 but output may differ slightly. Because our system tests programs by comparing output, please obey the following when writing your expression for this problem. First use the dollars/gallon and miles/gallon values to calculate the dollars/mile. Then use the dollars/mile value to determine the cost per 10, 50, and 400 miles.Note: Real per-mile cost would also include maintenance and depreciation.
Lab 3.7 Simple statistics.Part 1
Given 3 integers, output their average and their product, using integer arithmetic.Ex: If the input is 10 20 5, the output is:
11 1000
Note: Integer division discards the fraction. Hence the average of 10 20 5 is output as 11, not 11.666666666666666.Submit the above for grading. Your program will fail the test cases (which is expected), until you complete part 2 below but check that you are getting the correct average and product using integer division.
Part 2
Also output the average and product, using floating-point arithmetic.Ex: If the input is 10 20 5, the output is:
11 1000
11.666666666666666 1000.0
Lab 3.8 Using math functionsGiven three floating-point numbers x, y, and z, output x to the power of y, x to the power of (y to the power of z), the absolute value of x, and the square root of (xy to the power of z).
Ex: If the input is 5.0 6.5 3.2, the output is:
34938.56214843421 1.2995143401732918e+279 5.0 262.42993783925596
Hint: Coral has built-in math functions (discussed elsewhere) that may be used.
Learn More
Function Behavior Example
SquareRoot(x) Square root of x SquareRoot(9.0) evaluates to 3.0.
RaiseToPower(x, y) Raise x to power y: RaiseToPower(6.0, 2.0) evaluates to 36.0.
AbsoluteValue(x) Absolute value of x AbsoluteValue(-99.5) evaluates to 99.5.



