Search results for '''
-
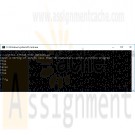
ITS320 Module 2 Option 1 Creating a Python Application for string validation
Regular Price: $10.00
Special Price $8.00
ITS320 Module 2 Option 1 Creating a Python Application for string validation
Option #1: Creating a Python Application
Python has built-in string validation methods for basic data. It can check if a string is composed of alphabetical characters, alphanumeric characters, digits, etc.
str.isalnum() This method checks if all the characters of a string are alphanumeric (a-z, A-Z and 0-9).
>>> print 'ab123'.isalnum()
True
>>> print 'ab123#'.isalnum()
False
str.isalpha() This method checks if all the characters of a string are alphabetical (a-z and A-Z).
>>> print 'abcD'.isalpha()
True
>>> print 'abcd1'.isalpha()
False
str.isdigit() This method checks if all the characters of a string are digits (0-9).
>>> print '1234'.isdigit()
True
>>> print '123edsd'.isdigit()
False
str.islower() This method checks if all the characters of a string are lowercase characters (a-z).
>>> print 'abcd123#'.islower()
True
>>> print 'Abcd123#'.islower()
FalseSAMPLE
str.isupper() This method checks if all the characters of a string are uppercase characters (A-Z).
>>> print 'ABCD123#'.isupper()
True
>>> print 'Abcd123#'.isupper()
FalseAssignment Instructions:
Write a Python program that performs the following tasks:
1. Read from the console an arbitrary string S of length less than 50 characters.
2. In the first output line, print True if S has any alphanumeric characters. Otherwise, print False.
3. In the second line, print True if S has any alphabetical characters. Otherwise, print False.
4. In the third line, print True if S has any digits. Otherwise, print False.
5. In the fourth line, print True if S has any lowercase characters. Otherwise, print False.
6. In the fifth line, print True if S has any uppercase characters. Otherwise, print False.
7. Develop Python code that implements the program requirements.Assignment Deliverables:
Learn More
• Submit a text file containing your Python code into the Module 2 drop box. Name your file ITS320_CTA2_Option1.py -
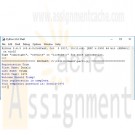
CIS115 Week 1 Lab Building a Registration Form and Pay Calculator in Python
Regular Price: $12.00
Special Price $10.00
CIS115 Week 1 Lab Building a Registration Form and Pay Calculator in Python
CIS115 Week 1 Lab Overview
Title of Lab: Building a Registration Form and Pay Calculator in Python
Summary – Part 1
Create a program that allows a student to complete a registration form and displays a completion message that includes the user's full name and a temporary password.Summary – Part 2
Create a program that calculates a user's weekly gross and take-home pay.Deliverables
• 2 source code Python files.
• A Word document containing both source code and the screen print of the program outputs.Lab Steps
Part 1 – Registration FormSample Output:
Registration Form
First Name: Eric
Last Name: Idle
Birth Year: 1934
Welcome Eric Idle!
Your Registration is complete.
Your temporary password is: Eric*1934Specifications:
• The user's full name consists of the user's first name, a space, and the user's last name.
• The temporary password consists of the user's first name, an asterisk (*), and the user's birth year.
• Assume the user will enter valid data.INPUT PROCESSING OUTPUT
first_name password=first_name + "*" + str(birth_year) password
last_name
birth_year
Part 2 – Pay CalculatorSample Output:
Pay Check Calculator
Hours Worked: 35
Hourly Pay Rate: 14.50
Gross Pay: 507.5
Tax Rate: 18
Tax Amount: 91.35
Take Home Pay: 416.15• The formula for calculating gross pay is:
o gross pay = hours worked * hourly rate
• The formula for calculating tax amount is:
o tax amount = gross pay * (tax rate / 100)
• The formula for calculating take home pay is:
o take home pay = gross pay - tax amount
• The tax rate should be 18%, but the program should store the tax rate in a variable so that you can easily change the tax rate later, just by changing the value that's stored in the variable.
• The program should accept decimal entries like 35.5 and 14.25.
• Assume the user will enter valid data.
• The program should round the results to a maximum of two decimal places.INPUT PROCESSING OUTPUT
Learn More
hours gross_pay = round(hours * pay_rate, 2) gross_pay
pay_rate tax_rate = 18 tax_rate
tax_amount = round(gross_pay * (tax_rate / 100), 2) tax_amount
take_home_pay = round(gross_pay - tax_amount, 2) take_home_pay -
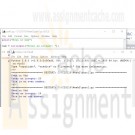
CIS115 Week 2 Lab Even or Odd and Grade Checker in Python
Regular Price: $12.00
Special Price $10.00
CIS115 Week 2 Lab Even or Odd and Grade Checker in Python
CIS115 Week 2 Lab Overview
Title of Lab: Even or Odd and Grade Checker in Python
Summary - Part 1
Create a program that checks whether a number is even or odd.Summary - Part 2
Create a program that checks one's letter grade.Deliverables
• 2 source code Python files.
• A Word document containing both source code and the screen print of the program outputs.Lab Steps
Part 1 - Even or OddSample Output:
Even or Odd
Enter an integer: 20
This is an even number.Specifications:
• Use the selection structure.
• Assume that the user will enter a valid integerPart 2 - Pay Calculator
Make sure to use the following criteria:
• 100 - 90: A
• 89 - 80: B
• 79 - 70: C
• 69 - 60: D
• 59 and below: FSample Output:
Grade Checker
Enter your grade: 88
You earned a B• Assume the user will enter valid data.
Learn More
• Selection structure needs to be used. -
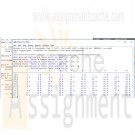
CIS115 Week 4 Lab Multiplication Table in Python
Regular Price: $12.00
Special Price $10.00
CIS115 Week 4 Lab Multiplication Table in Python
CIS115 Week 4 Lab Overview
Title of Lab: Multiplication Table in Python
Summary
This week's lab is to create a simple multiplication table using nested loops and if statements.
Prompt the user for the size of the multiplication table (from 2x2 to 10x10). Use a validation loop to display a warning if the number is less than 2 or greater than 10 and prompt the user to enter the data again until they enter a valid number.
Put a # after any even number in your table (odd numbers will have just a space/nothing after them).Deliverables
• A source code Python file.
• A Word document containing both source code and the screen print of the program outputs.Lab Steps
Sample Output:
The output should be something similar to the following.
What size multiplication table would you like? (2 - 10): 1
Invalid entry - Enter a number between 2 and 10
What size multiplication table would you like? (2 - 10): 15
Invalid entry - Enter a number between 2 and 10
What size multiplication table would you like? (2 - 10): 10--- Multiplication Table ( 10 x 10 ) ---
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 1 2 # 3 4 # 5 6 # 7 8 # 9 10 #
2 | 2 # 4 # 6 # 8 # 10 # 12 # 14 # 16 # 18 # 20 #
3 | 3 6 # 9 12 # 15 18 # 21 24 # 27 30 #
4 | 4 # 8 # 12 # 16 # 20 # 24 # 28 # 32 # 36 # 40 #
5 | 5 10 # 15 20 # 25 30 # 35 40 # 45 50 #
6 | 6 # 12 # 18 # 24 # 30 # 36 # 42 # 48 # 54 # 60 #
7 | 7 14 # 21 28 # 35 42 # 49 56 # 63 70 #
8 | 8 # 16 # 24 # 32 # 40 # 48 # 56 # 64 # 72 # 80 #
9 | 9 18 # 27 36 # 45 54 # 63 72 # 81 90 #
10 | 10 # 20 # 30 # 40 # 50 # 60 # 70 # 80 # 90 # 100 #
Hints:
• The outer loop will start each new row.
• The inner loop will control the display of each column in the row.
• Note that to keep the numbers right-aligned, there are different amounts of space before single digit numbers (those less than 10), double digit numbers (those between 10-99), and triple digit numbers (100).
• The row labels can be added to your inner loop (note that there are different amounts of space required after the number in the row labels.
• The column labels should use a separate loop(s) that run before the main outer loop.
• You can continue printing on the same line using end="" in your print statement. This will come in handy if you want to print several things on one line inside a loop. For example, assuming the value of name is Ada, the following will print "Hello Ada" on one line:
print("hello ", end="")
print(name, end="")Tips:
Learn More
• Start early!
• Do the basic table first without worrying about spacing or lining things up, and don't include row or column headings (add those later).
• Once you get the numbers in the correct position, think about adding the proper amount of space before each number to line things up.
• Once the columns line up, add the #/space for even/odd numbers.
• Once the basic table is working, then add the row and column headings, and finally the main title.
• Test as you go! -

CIS115 Week 6 Lab Shopping List in Python
Regular Price: $12.00
Special Price $10.00
CIS115 Week 6 Lab Shopping List in Python
CIS115 Week 6 Lab Overview
Title of Lab: Shopping List in Python
Summary
Create a program that will allow a user to add, list, and delete items from a shopping list.Deliverables
• A source code Python file.
• A Word document containing both source code and the screen print of the program outputs.Lab Steps
The program should be modular. For example, you will want to have an add_item(shopping_list) function, a delete_item(shopping_list) function, a display_list(shopping_list) function, a display_menu() function, and a main().Sample Output:
Welcome to the program!
1. Add an item
2. List all items
3. Delete an item
4. ExitEnter a menu option: 2
1 : bananas
2 : applesEnter a menu option: 1
Please enter the item: pears
pears was added to the shopping listEnter a menu option: 2
1 : bananas
2 : apples
3 : pearsEnter a menu option: 3
Which number to delete: 3
pears was deletedEnter a menu option: 2
1 : bananas
2 : applesEnter a menu option: 4
have a great day!Specifications:
Learn More
• The program should start with 2 items in the shopping list.
• Don't forget to include at the end of the program the code:
o if __name__ == "__main__":
main();
• Use this code for the delete_item(shopping_list) function:
def delete_item(shopping_list):
number=int(input("Which number to delete: "))
if number<1 or number>len(shopping_list):
print("Invalid number\n")
else:
item=shopping_list.pop(number-1)
print(item," was deleted\n")
print() -
CYB/130 Week 3 Python LAB 4.16: Output range with increment of 10
Regular Price: $8.00
Special Price $3.00
CYB/130 Week 3 Python LAB 4.16: Output range with increment of 10
Write a program whose input is two integers. Output the first integer and subsequent increments of 10 as long as the value is less than or equal to the second integer.
Ex: If the input is:
-15
30
the output is:
-15 -5 5 15 25Ex: If the second integer is less than the first as in:
20
5
the output is:
Second integer can't be less than the first.For coding simplicity, output a space after every integer, including the last.
Learn More -
CYB/130 Week 3 Python LAB 4.14 LAB: Count input length without spaces, periods, or commas
Regular Price: $8.00
Special Price $3.00
CYB/130 Week 3 Python LAB 4.14 LAB: Count input length without spaces, periods, or commas
Given a line of text as input, output the number of characters excluding spaces, periods, or commas.
Ex: If the input is:
Listen, Mr. Jones, calm down.
the output is:
21Note: Account for all characters that aren't spaces, periods, or commas (Ex: "r", "2", "!").
Learn More -

CYB/130 Week 4 Python LAB 5.18: Miles to track laps
Regular Price: $8.00
Special Price $3.00
CYB/130 Week 4 Python LAB 5.18: Miles to track laps
One lap around a standard high-school running track is exactly 0.25 miles. Write the function miles_to_laps() that takes a number of miles as an argument and returns the number of laps. Complete the program to output the number of laps.Output each floating-point value with two digits after the decimal point, which can be achieved as follows:
print('{:.2f}'.format(your_value))Ex: If the input is:
1.5
the output is:
6.00Ex: If the input is:
2.2
the output is:
8.80Your program must define and call the following function:
Learn More
def miles_to_laps(user_miles) -

CYB/130 Week 4 Python LAB 5.19: Driving costs - functions
Regular Price: $8.00
Special Price $3.00
CYB/130 Week 4 Python LAB 5.19: Driving costs - functions
Driving is expensive. Write a program with a car's miles/gallon and gas dollars/gallon (both floats) as input, and output the gas cost for 10 miles, 50 miles, and 400 miles.Output each floating-point value with two digits after the decimal point, which can be achieved as follows:
print('{:.2f}'.format(your_value))Ex: If the input is:
20.0
3.1599
the output is:
1.58
7.90
63.20Your program must define and call the following driving_cost() function. Given input parameters driven_miles, miles_per_gallon, and dollars_per_gallon, the function returns the dollar cost to drive those miles.
Ex: If the function is called with:
50 20.0 3.1599
the function returns:
7.89975def driving_cost(driven_miles, miles_per_gallon, dollars_per_gallon)
Learn More
Your program should call the function three times to determine the gas cost for 10 miles, 50 miles, and 400 miles.
Note: This is a lab from a previous chapter that now requires the use of a function. -

CYB/130 Week 4 Python LAB 5.20: Step counter
Regular Price: $8.00
Special Price $3.00
CYB/130 Week 4 Python LAB 5.20: Step counter
A pedometer treats walking 2,000 steps as walking 1 mile. Write a program whose input is the number of steps, and whose output is the miles walked.Output each floating-point value with two digits after the decimal point, which can be achieved as follows:
print('{:.2f}'.format(your_value))Ex: If the input is:
5345
the output is:
2.67Your program must define and call the following function. The function should return the amount of miles walked.
Learn More
def steps_to_miles(user_steps)




