Search results for 'q'
-

CMIS 102 Assignment 2 build a state-of-the-art gaming computer
$12.00CMIS 102 Assignment 2 build a state-of-the-art gaming computer
Design a program to perform the following task:
Calculate the total price to purchase all the components required to build a state-of-the-art gaming computer from components available on the internet.[Hints: Before attempting this exercise, be sure you have completed all of chapter 3 and course module readings, participated in the weekly conferences, and thoroughly understand the examples throughout the chapter. As before, there are 3 main components of your submission including the problem analysis, program design and documentation, and sample test data.]
Part 1: Analysis [5 points]
Using a similar approach as example 3.6 (textbook page 146): “A new Car Price Calculator”, provide your analysis for the following problem statement: You need to write a program that will calculate the total price to purchase all the components required to build a state-of-the-art gaming computer from newegg.com. You will need to conduct some analysis on newegg.com (or amazon.com) regarding the possible options and prices to be considered. However; assume the computer will consist of the following components:CPU
Case
Power supply
Motherboard
Hard Drive
RAM
DVD
Sound Card
Monitor
Graphics Card
Operating SystemI would recommend you keep the option choices limited to 3 different components, or your program will really grow fast. For example, you could provide options for the Operating System (Windows 7, Red Hat Linux), the RAM (4 MB, 8 MB, 12 MB) and the Hard Drive Size (500 GB, 1 TB, 1.5 TB) and leave everything else as a baseline. I leave it up to you to determine which components you want to add options for and for researching the approximate prices. Be sure your prices are fairly realistic.
Your analysis should be clearly written and demonstrate your thought process and steps used to analyze the problem. Be sure to include what is the required output? What is the necessary input and how you will obtain the required output from the given input? Also, include your variable names and definitions. Be sure to describe the necessary formulas and sample calculations that might be needed.Part 2: Design [5 points]
Using a similar approach as example 3.6 (textbook page 146): “A new Car Price Calculator”, provide your program design for the program you analyzed for calculating the total price of your gaming computer. Be sure to describe the fundamental tasks (i.e., things your program must do) needed to solve the problem so you can use a modular design. Provide pseudocode of your overall design that includes the Main module and the order of the module calls (see page 148 for an example) and a Hierarchy chart for the computer price calculator (see figure 3.8 page 148). Finally, list all of your pseudocode for each module. (See pages148-150 as an example.)Include header and step comments in your pseudocode, using a similar approach as the example provided in section 2.3 (textbook page 86). See example 2.8 on pages 87-88).
Part 3: Test Data [3 points]
Learn More
Prepare at least 5 sets of input data (Test data) along with their expected output for testing your program. Your test data can be presented in the form of a table as was shown in Assignment 1. Be sure that you provide expected output for each test case. -
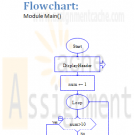
CMIS 102 Assignment 3 Repetition Statements multiplication table
$12.00CMIS 102 Assignment 3 Repetition Statements multiplication table
Write a program that would calculate and display the results for the multiplication table for values ranging from 1 to 100.
Before attempting this exercise, be sure you have completed all of chapter 4, 5 and course module readings, participated in the weekly conferences, and thoroughly understand the examples throughout the chapter. There are 3 main components of your submission including the problem analysis, program design and documentation, and sample test data.
1. Provide your analysis for the following problem statement: You need to write a program that would calculate the results for the multiplication table up from 1 to 100. (For example, 1X1, 1X2, 1X3 ... 1X10, 2X1, 2X2 ... 10X2 ... 10x10). Your program should print the output for each step and output a new line after 10 items. So the example output would be something like this Notice a new line appears after 10 steps:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
2 4 6 8 10 ... 20
...
10 20 30 ... 100To write the new lines you can just use code similar to : write “new line”. Hint: You will probably use a nested repetition loop.
Your analysis should be clearly written and demonstrate your thought process and steps used to analyze the problem. Be sure to include what is the required output? What is the necessary input and how you will obtain the required output from the given input? Also, include your variable names and definitions. Be sure to describe any necessary formulas and sample calculations.
2. Provide your program design for the program you analyzed for printing the multiplication table. Be sure to describe the fundamental tasks (i.e., things your program must do) needed to solve the problem so you can use a modular design. Provide pseudocode of your overall design that includes the Main module and the order of the module calls, and a Hierarchy chart for the program (see figure 3.8 page 148). Finally, display the flow charts (using Raptor, or your favorite graphics editor) for each module. (See figure 5.3 page 233 as an example.)
Include header and step comments in your pseudocode, using a similar approach as the example provided in section 2.3 (textbook page 86). See example 2.8 on pages 88).
3. Prepare any input data (Test data) along with expected output for testing your program (Note: Programs may not always have both input and output data. Just provide test cases for your application). Your test data can be presented in the form of a table as was shown in Assignment 1.
Learn More -

CMIS 102 Assignment 4 Functions Calculate Perimeter of a Rectangle
$12.00Assignment 4 Functions Calculate Perimeter of a Rectangle
In this assignment, you will design a program to perform the following task:
Write a program, using functions, that calculates the area and perimeter of a rectangle whose dimensions (length and width) are provided by a user.Before attempting this exercise, be sure you have completed all of chapter 8 and course module readings, participated in the weekly conferences, and thoroughly understand the examples throughout the chapter. There are three main components of your submission, including the problem analysis, program design and documentation, and sample test data.
1. Provide your analysis for the following problem statement: You need to write a program that calculates the area and perimeter of a rectangle whose dimensions (length and width) are provided by a user.
Your analysis should be clearly written and demonstrate your thought process and steps used to analyze the problem. Be sure to include what the required output is. What is the necessary input and how will you obtain the required output from the given input? Also, include your variable names and definitions. Be sure to describe any necessary formulas and sample calculations.2. Provide your program design for the problem you analyzed for calculating and displaying the area and perimeter of a rectangle. Always work for modular design when possible. Be sure to use separate functions for calculating the area and perimeter of the rectangle. Other subprograms for Input and Output should be included as needed. Be sure to describe the fundamental tasks (i.e., things your program must do) needed to solve the problem so you can use a modular design. Provide pseudocode of your overall design that includes the Main module and the order of the module calls, and a Hierarchy chart for the program (see figure 3.8, page 148). Finally, display the flowcharts (using Raptor, or your favorite graphics editor) for each module. (See figure 5.3, page 225 as an example.)
Include header and step comments in your pseudocode, using a similar approach as the example provided in section 2.3 (textbook page 86). (See example 2.8 on pages 87–88.)
3. Prepare at least three sets of input data (Test data) along with expected output for testing your program. Your test data can be presented in the form of a table as was shown in Assignment 1.
Learn More -

CMIS 102 Final Project Average age of your family
$15.00CMIS 102 Final Project Average age of your family
Your final project will be to analyze, design, and document a simple program that utilizes a good design process and incorporates sequential, selection and repetitive programming statements as well as at least one function call and the use of at least one array. The specific problem you need to solve for the final project is: Design a program that will allow a user to Input a list of your family members along with their age and state where they reside. Determine and print the average age of your family and print the names of anyone who live in Texas.
Final Project Deliverables:
There are two deliveries for this project. The first delivery is the project plan which provides your problem statements, problem analysis, and how it will comply with the project specifications. The project plan is worth 10% of your grade. The final delivery will be your completed project design along with your code comments and comprehensive test plan. The final delivery is worth 20% of your grade.Your project plan is due in week 7 by midnight EST, on the specific date posted in the class schedule. The final delivery is due no later than the last day of class. Your instructor’s policy on late projects applies to this project.
Example Project Plan and Final Project template files, containing the required sections are included in the available resources. You should use this document to start your writing and fill in all of the details required.
Format:
Learn More
Project plan format and length:
The documentation describing your analysis and test plan should be written using Microsoft Word. The font size should be 12 point. The page margins should be 1 inch. The paragraphs should be formatted with double line or single line spacing. Any figures, tables, equations should be neatly labeled. All references should use APA style. -

Assignment 2 Frans Virtual Fruit Stand Part 2
$12.00Assignment 2 Fran’s Virtual Fruit Stand, Part 2
Use the concepts and scenario from Assignment 1 to help Fran’s Virtual Fruit Stand increase the functionality of its online shopping cart. When a customer checks out, the shopping cart must store the required data pertaining to each item the customer is buying. Your job is to design a program that will prompt the user for the required data and then store it. The required data includes the item name, the price per pound, and the number of pounds of that item being purchased. When complete, your program should include three (3) arrays, two (2) loops, one (1) and / or conditional statement, and one (1) variable.
Using Visual Logic, design a flowchart that is also a fully functional program to add functionality to the online shopping cart. According to your design, the program must:
Continually accept data regarding the purchase of fruit as specified below until the user enters a sentinel value, or until five (5) items are entered, whichever comes first.
Prompt the user for each item and accept the name of the fruit (e.g., “dried apples”), the price per pound, and the number of pounds sold in a month.
Store the required data in three (3) arrays (e.g., one (1) for the item name, one (1) for the price per pound, and one (1) for the number of pounds being purchased) with corresponding index values. Note: For example, index value 3, when applied to the “itemName” array, would give us the name of the third item that the customer is buying. That same index value of 3, when applied to the “pricePerPound” array, would give us the price per pound of that same third item that the customer is buying.
Store up to five (5) values in each of the three (3) arrays.
Provide functionality in which the user ends the program by typing a sentinel value, and the program tells the user what the sentinel value is. Note: An acceptable message may read “Type n to end the program.”, where “n” is the sentinel value. If the user does not end the program in this way, then the program ends when it has collected the data for five (5) items.
Print an itemized receipt with the following data after the last item in the purchase has been saved to the array.
Item name
Price per pound of each item
Number of pounds purchased of each item
Subtotal price for each item, calculated as price per pound multiplied by the number of pounds
Total weight of the entire order (in pounds)
The cost of shipping which is based on the total weight of the entire order, calculated as 50 cents per pound. Note: For example, if the entire order weighs seven (7) pounds, the cost of shipping would be $3.50.
Grand total price of all items and shipping.Note: Use the “console” option in the output command to accomplish this task. An example of an acceptable output has been provided below:
Learn More -
Assignment 1 Frans Virtual Fruit Stand Part 1
$12.00Assignment 1 Fran’s Virtual Fruit Stand, Part 1
Fran’s Virtual Fruit Stand is an online store that sells several types of dried fruit. Based on the needs of Fran’s Virtual Fruit stand, you must design a flowchart using Visual Logic. The flowchart must also be a fully functional program which follows the design requirements below.
Note: This program does not require the use of arrays. The program will prompt for data on a single item, process that data, display any relevant messages as described below, and then move on to the next item. Use the “console” option in the output command to display the output in a single window. Displaying the output can be accomplished with as few as three (3) variables that simply get overwritten each time the loop repeats.
Using Visual Logic, design a flowchart that is also a fully functional program. According to your design, the program must:
Continually accept data regarding the purchase of fruit until a sentinel value is entered.
Prompt the user for each item, and accept the name of the fruit (e.g., “dried apples”), the price per pound, and the number of pounds sold in a month.
Display a clear message for items that are considered:
Best-selling items
Note: Best-selling items are identified as those that sell 5,000 or more pounds per month on average. For example, an acceptable message may read, “Yellow raisins are a best-selling item.”Big-ticket items
Note: Big-ticket items are identified as those that are best-selling items and also cost $4 per pound or more. For example, an acceptable message may read, “Freeze-dried blueberries are a big-ticket item.”High-priced items
Note:High-priced items are identified as those that sell for $7 per pound or more. For example, an acceptable message may read, “Dried mangos are a high-priced item.”Lowest-selling items
Note: Lowest-selling items are identified as those that sell 500 pounds or less per month on average. For example, an acceptable message may read, “Dried Ugli Fruit is a lowest-selling item.”High-income generating items
Note: High-income generating items are identified as those that generate $7,000 or more per month on average. To determine the income generated per item, multiply the price per pound by the number of pounds sold per month. If the item generates $7,000 or more per month, an acceptable message may read, “Dried pineapple chunks are a high-income generating item.”Loop through all of the above steps until the user types the sentinel value when prompted. Display the sentinel value so that the user may ultimately be able to demonstrate an understanding of the way in which to end the program. Note: An acceptable message may read “Type n to end the program.”, where “n” is the sentinel value.
Your Visual Logic program must follow these formatting requirements:
Be accomplished in a single Visual Logic program.
Be submitted as a single file with the “.vls” file extension.
Be fully functional in order to receive full credit.
Learn More
The specific course learning outcomes associated with this assignment are:
Demonstrate the use of algorithms and pseudocoding to the problem-solving process.
Distinguish among the basic types, steps, and properties of programming.
Apply the techniques of functional decomposition, modularization techniques, and debugging strategies into program design.
Describe the features and fundamental data structures of programming design.
Select and create the appropriate conditional and iteration constructs for a given programming task. -

CMIS 102 Final Project Average age of your family and members living in Tennessee
Regular Price: $15.00
Special Price $12.00
CMIS 102 Final Project Average age of your family and members living in Tennessee
Your final project will be to analyze, design, and document a simple program that utilizes a good design process and incorporates sequential, selection and repetitive programming statements as well as at least one function call and the use of at least one array. The specific problem you need to solve for the final project is:
Design a program that will allow a user to Input a list of your family members along with their age and state where they reside. Determine and print the average age of your family and print the names of anyone who lives in Tennessee.There are 4 components of your submission including:
Program Description - A detailed, clear description of the program you are building.
Analysis - Demonstrates your thought process and steps used to analyze the problem. Be sure to include the required input and output and how you will obtain the required output from the given input? Also, include your variable names and definitions. Be sure to describe the necessary formulas and sample calculations that might be needed. Talk about the functions you plan to use and how you will use arrays. Be sure to talk about the types of programming statements that will be used on why.
Test plan - Prepare at least 3 sets of input data (Test data) along with their expected output for testing your program. Your test data can be presented in the form of a table as follows (note: feel free to adapt to your design)
Pseudocode - Provide pseudocode of your overall design that fulfills the requirements of the projectAll of these components should be placed in word document for submission.
Additional details about the program you need to write:
Learn More
Family sizes vary, however you should design to be able to enter at least 50 Family members.
Your test cases should have at least 5 family members.
Be sure to separate some functionality into functions or submodules. Having all functionality in the main module is not a good design.
Your design should consider how to indicate the family member entry is complete.
Carefully consider the best data type for each of your variables. (e.g. when to use Float versus Integers versus Strings) -

Handicap of a golfer Module 2 Pseudo Code
Regular Price: $15.00
Special Price $12.00
Handicap of a golfer Module 2 Pseudo Code
Because an official handicap requires 10 scores, you will need to modify the module 1 program to accept multiple scores, process the scores, and provide the user with their handicap.
Learn More
Tell the user that they will need to enter 10 scores, which include the slope and rating for the course. Create a loop that will run 10 times. In this loop you will print the score the user just entered, calculate the handicap and add the handicap to a handicap total variable.
After you executed the loop 10 times; exit the loop, divide the total handicap by 10, and display the user’s average handicap. -

Handicap of a golfer Module 3 Pseudo Code
Regular Price: $15.00
Special Price $12.00
Handicap of a golfer Module 3 Pseudo Code
Because an official handicap requires up to 10 scores, you will need to modify the previous program to accept multiple scores, process the scores, and provide the user with their handicap.
Create a Do-While loop that runs up to 10 time that asks the user to enter up to 10 scores, which include the slope and rating for the course, and calculates the handicap for each score. You will need to use either parallel arrays or a two-dimensional array in order to store the score, slope and rating for each entry, and variables for the handicap accumulator and number of scores entered. The user will enter a 0 in score to exit the loop before entering 10 scores.
Once all scores have been entered, insert a new loop to read the array and display all of the scores. After you exit this loop, you need to display the average handicap with this as well.
Learn More -

CMIS 102 Assignment 1 Usable Area of house
Regular Price: $15.00
Special Price $12.00
CMIS 102 Assignment 1 Usable Area of house
In this assignment, you will design a program to perform the following task:
Calculate the usable area in square feet of house. Assume that the house has a maximum of four rooms, and that each room is rectangular1. Using a similar approach as example 2.3 (textbook page 75): "Finding the Sale Price of Items in a Department Store", provide your analysis for the following problem statement:
You need to write a program that will calculate the number of square feet (living space) in a 4-room house. Your analysis should be clearly written and demonstrate your thought process and steps used to analyze the problem. Be sure to include what is the required output? What is the necessary input and how you will obtain the required output from the given input? Also, include your variable names and definitions. Be sure to describe the necessary formulas and sample calculations that might be needed.2. Using a similar approach as the example provided in section 2.2(textbook page 78) for "The Sale Price Program continued", provide your program design for the program you analyzed for calculating the number of square feet in a house. Be sure to describe the fundamental tasks needed to solve the problem so you can use a modular design. Provide pseudocode of your overall design that includes the Main module and the order of the module calls (see page 82 for an example). Finally, list all of your pseudocode for each module (See example 2.6 on page 83 as an example).
Include header and step comments in your pseudocode, using a similar approach as the example provided in section 2.3 (textbook page 86). See example 2.8 on pages 87-88).3. Prepare at least 3 sets of input data (Test data) along with their expected output for testing your program. Your test data can be presented in the form of a table as follows (note: feel free to adapt to your design)
Learn More




